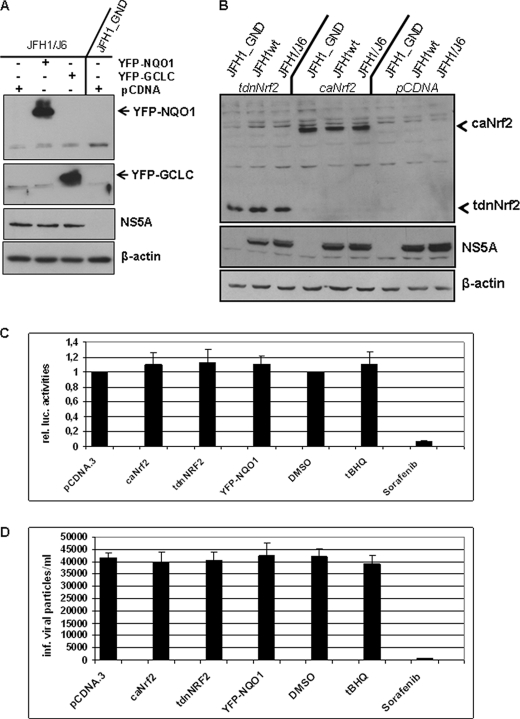
FIGURE 2.
Overexpression of ARE-regulated genes does not affect HCV replication. A, HCV-replicating cells were transfected with expression vectors encoding NQO1 or GCLC as YFP fusion protein. Transfection with the equal amount of pCDNA served as control. Overproduction of YFP-NQO1 or YFP-GCLC was demonstrated by Western blotting. The effect on viral replication was determined using a NS5A-specific antiserum. Lysate from HCV-negative cells (JFH1_GND) served as negative control. B, HCV-replicating cells (JFH1wt, JFH1/J6) were transfected with expression vectors coding for a trans-dominant negative mutant (ptdnNrf2; lanes 1–3) or a constitutively active mutant (pcaNrf2; lanes 4–6) or with the empty expression vector pCDNA (lanes 7–9). Lysate from HCV-negative cells (JFH1_GND) served as negative control. The effect on viral replication was determined by Western blot analysis using a NS5A-specific antiserum. Overproduction of tdnNrf2 or caNrf2 was demonstrated by Western blotting. C, analysis of viral replication by luciferase reporter gene assay. 48 h after electroporation, HCV luc-JFH-1-replicating Huh7.5 cells were co-transfected with pcaNrf2, ptdnNrf2, pYFP-NQO1, or pCDNA.3. Incubation with tBHQ was performed for 16 h. Here, treatment with an equivalent amount of DMSO (0.1%) served as a control treatment with Sorafenib (10 μm) was performed to inhibit HCV replication (26). D, infection of HuH7.5 cells with supernatants derived from pNQO1, ptdnNrf2-, pcaNrf-2, pCDNA3- transfected cells, or tBHQ-stimulated cells. Cells were transfected 48 h after electroporation. Again 48 h later, the supernatant was collected. In case of the tBHQ-treated cells were stimulated 16 h before harvesting with tBHQ. The supernatant from electroporated-untreated cells served as control. The amount of HCV particles was determined by limited dilution. Mean values from three independent experiments are shown. The bars represent the standard deviation.