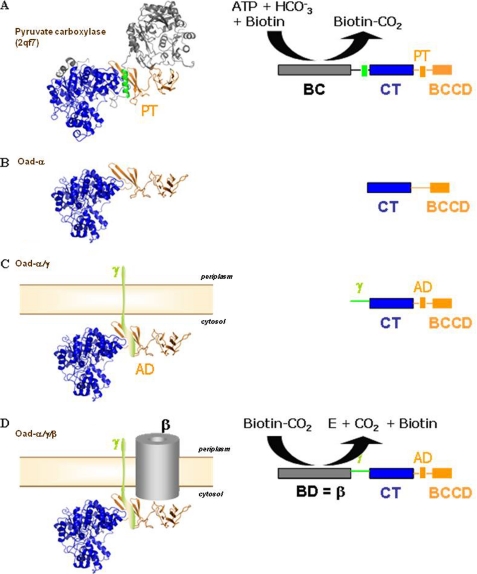
FIGURE 4.
Equivalence between PC and OAD systems. Stepwise comparison of different domains in the multimodular proteins is shown. A, high resolution structure and schematic single-chain monomer representation of R. etli PC (PDB code: 2qf7) are shown. PC monomers are composed of four domains: the N-terminal BC, the central CT domain, the tetramerization or allosteric domain (TD), and the BCC domain. B, homology modeling of Oad-α from V. cholera is based on R. etli PC. Oad-α is composed of the N-terminal CT and the C-terminal BCC domains (BCCD) that are homologs to those in 2qf7. C, schematic compares a putative chimera composed of Oad-α/Oad-γ subunits and PC. A similar module organization is noticeable between the two systems: the AD in Oad-α is equivalent to the tetramerization domain in PC, and the soluble α-helical element in Oad-γ likely mimics the α-helix in PC that stabilizes the PT domain (green color in A; see also Fig. 3B). D, although performing the opposite chemical reaction, the Oad-β subunit, acting as a biotin decarboxylase (BD), sharing functional similarities with BC in PC.