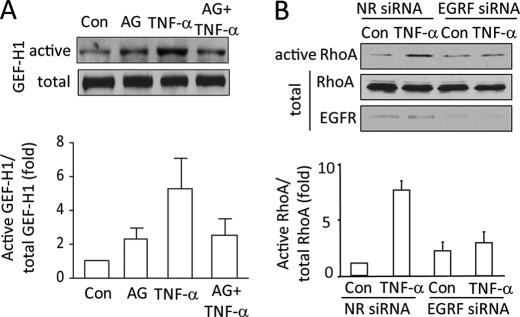
FIGURE 2.
Inhibition of EGFR prevents TNF-α-induced GEF-H1 and RhoA activation. A, confluent LLC-PK1 cells were serum-depleted, then pretreated with 100 nm AG1478 (AG, 30 min) in serum-free DMEM followed by the addition of 10 ng/ml TNF-α for 10 min. Active GEFs were precipitated using GST-RhoA(G17A). GEF-H1 in the precipitates and total cell lysates (active and total, respectively) was detected by Western blotting. B, MDCK cells were transfected with NR siRNA or EGFR-specific siRNA. Forty-eight hours after transfection cells were treated with 10 ng/ml TNF-α (10 min), and active RhoA was captured using Rhotekin GST-RBD. RhoA in the precipitates (active) and total cell lysates was detected by Western blotting. The total cell lysates were redeveloped using an EGFR antibody. The blots were quantified by densitometry (see “Experimental Procedures”). The graphs below the blots show the mean ± S.E. from n = 3 independent experiments.