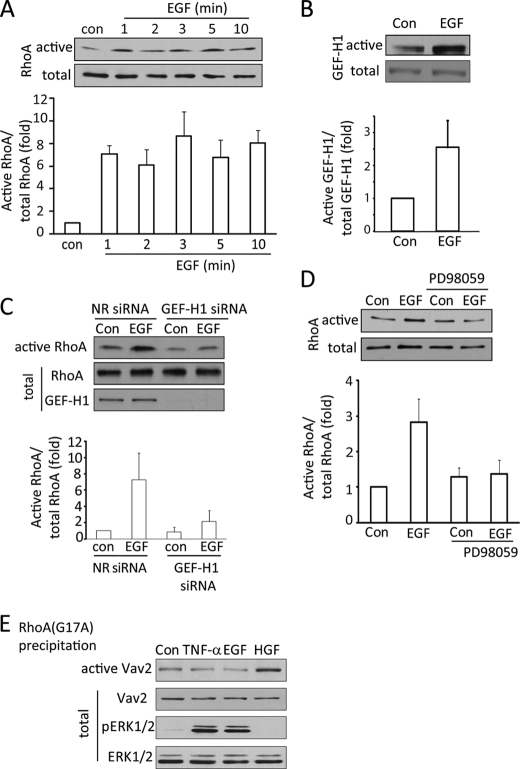
FIGURE 3.
EGF activates the ERK/GEF-H1/RhoA pathway. A–D, LLC-PK1 cells were serum-depleted for 3 h. In C, 48 h before the experiment, cells were transfected using NR or GEF-H1-specific siRNA. The cells were exposed to 10 ng/ml EGF for the indicated times (A) or 1 min (B) or 10 min (D) or 2 min (C). In D, cells were treated with 10 μm PD98059 before and during stimulation with EGF. At the end of the treatments cells were lysed, and the amount of active RhoA (A, C, and D) or GEF-H1 (B) was detected and analyzed as described earlier. The graphs below the blots show data from the densitometric analysis (mean ± S.E. n = 3). E, LLC-PK1 cells were serum-depleted and treated using 10 ng/ml TNF-α (10 min) or 100 ng/ml EGF (10 min) or 10 ng/ml HGF (30 min). Cells were lysed, and active GEFs were precipitated using RhoA(G17A) as in B. Vav2 in the precipitates or cell lysates (active and total, respectively) were detected by Western blotting. The total cell lysates were redeveloped to detect pERK and ERK levels.