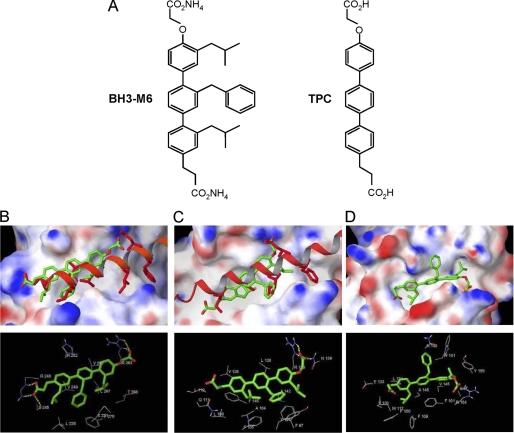
FIGURE 1.
Molecular docking studies of the interactions between BH3-M6 and Mcl-1, Bcl-XL, and Bcl-2. A, chemical structures of BH3-M6 and TPC. B–D, BH3-M6 docked to Mcl-1, Bcl-XL, and Bcl-2. B, crystal structure of human Bim BH3 helix bound to human Mcl-1 with the side chains of Bim Glu-55, Ile-58, Leu-62, Ile-65, Asp-67, and Phe-69, relative to the BH3-M6 position. The protein Mcl-1 is shown by its molecular surface. Area with positive electrostatic potential is colored blue and that with negative electrostatic potential colored red (the same presentation is used for proteins Bcl-XL and Bcl2). B, lower panel, residues of Mcl-1 interacting with BH3-M6. Yellow dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds. C, crystal structure of mouse Bim BH3 helix bound to mouse Bcl-XL with the side chains of Bim Ile-90, Leu-94, Ile-97, and Asp-99, relative to the BH3-M6 position. C, lower panel, residues of Bcl-XL interacting with BH3-M6. Yellow dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds. D, BH3-M6 docked to the original NMR structure of Bcl-2. D, lower panel, residues of Bcl-2 that interact with BH3-M6. The alignment between human and mouse Bim BH3 α-helix is as follows: Human (58-I A Q E L R R I G D E F N A Y-72) Mouse (90-I A Q E L R R I G D E F N E T-104).