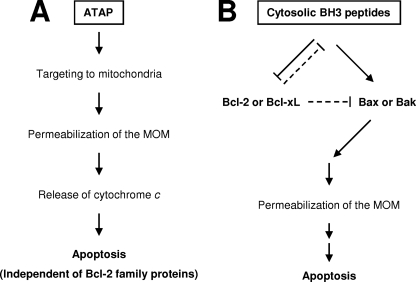
FIGURE 6.
Proposed events for the pro-apoptotic actions of ATAP and BH3 peptides at mitochondria. A, ATAP derived from tail-anchor domain of Bfl-1 can target to mitochondrial membrane by its intrinsic nature of the mitochondrial targeting signal (35). Once at mitochondria, ATAP may insert into the MOM through a translocation complex on the MOM or through a direct interaction with the lipid bilayer. An amphipathic helical feature on the transmembrane segment of ATAP is likely involved in the perturbation of mitochondria membrane integrity by pore formation. The pore formation and pro-apoptotic function of ATAP are independent of Bcl-2 family proteins. B, distinctively, BH3 peptides derived from pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins accumulate in the cytoplasm, and hence only a small fraction would interact with Bcl-2 family proteins on the MOM. For the pro-apoptotic activity of BH3 peptides, the intracellular content of Bcl-2 family proteins is critical. First, the BH3 peptides must be in excess of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins such as Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL to inhibit their anti-apoptotic function. Otherwise, the peptides might be sequestered by these anti-apoptotic proteins on the MOM (shown by dashed lines). Second, there must be enough pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins such as Bax or Bak because the pro-apoptotic activity of BH3 peptides was dependent on these proteins. Under this situation, BH3 peptides can induce apoptosis by either directly binding and activating Bax and/or Bak or preventing anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins from blocking Bax, Bak, and/or BH3-only pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins (12, 19, 20).