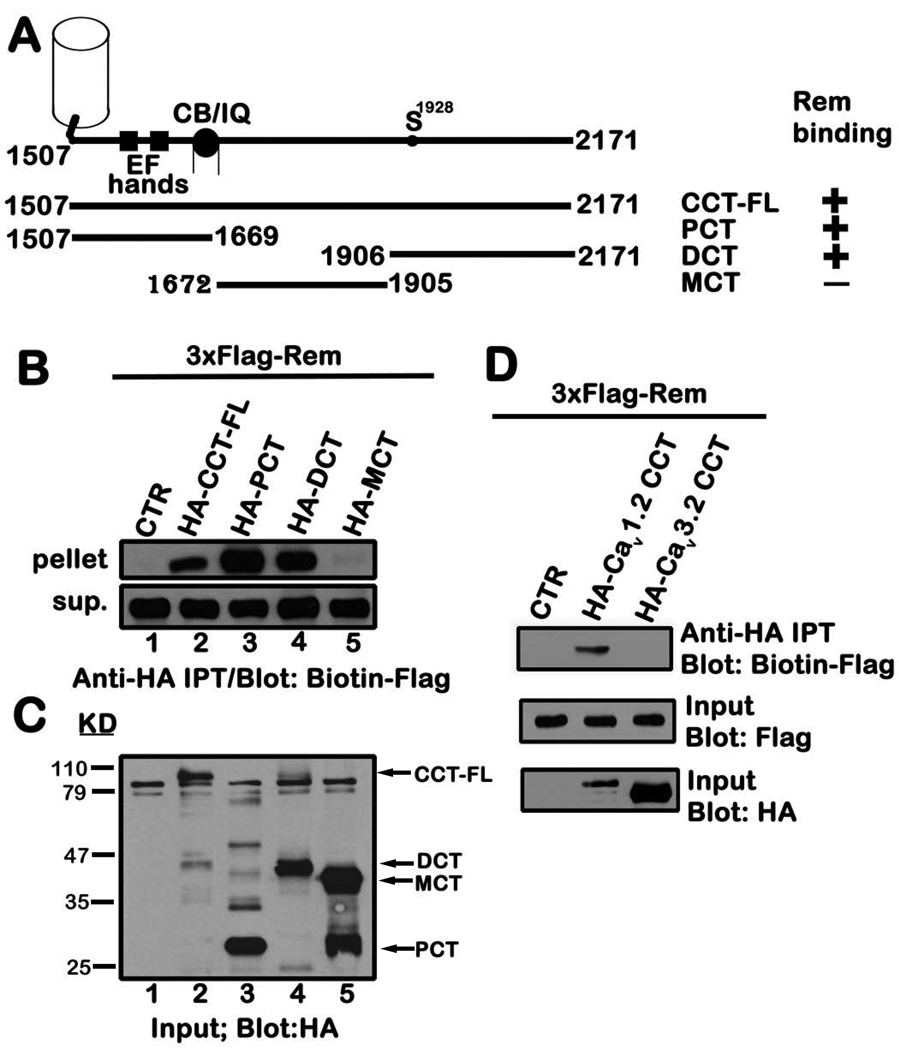
Figure 1. Rem interacts with the proximal and distal domains of CCT.
A, Schematic of the CCT truncation mutants with the Rem interaction status indicated on the right. B, TsA201 cells were transiently co-transfected with expression vectors encoding 3xFlag-tagged Rem and either pCDNA3.1+3xHAa (empty vector), HA-CCT-FL or the indicated HA-tagged CCT truncation mutants. 48 h post-transfection, cells were harvested, and cell lysate (0.5 mg) was subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibody as described under “Materials and Methods”. The entire bound fraction or a portion of the unbound fraction (2.5 µl) was analyzed by immunoblotting with biotin-Flag to detect Rem. C, Cell lysate (5 µg) was immunoblotted with anti-HA antibody to monitor expression of CCT-FL and the corresponding truncation mutants used in panel B. D, TsA201 cells were transiently co-transfected with vectors expressing Flag-Rem and either pCDNA3.1+3xHAa, HA-Cav1.2 CCT or HA-Cav3.2 CCT. Co-immunoprecipitation was performed using HA antibody as described in B and Rem binding examined by biotin-Flag immunoblotting. Results in each panel are representative of three independent experiments.