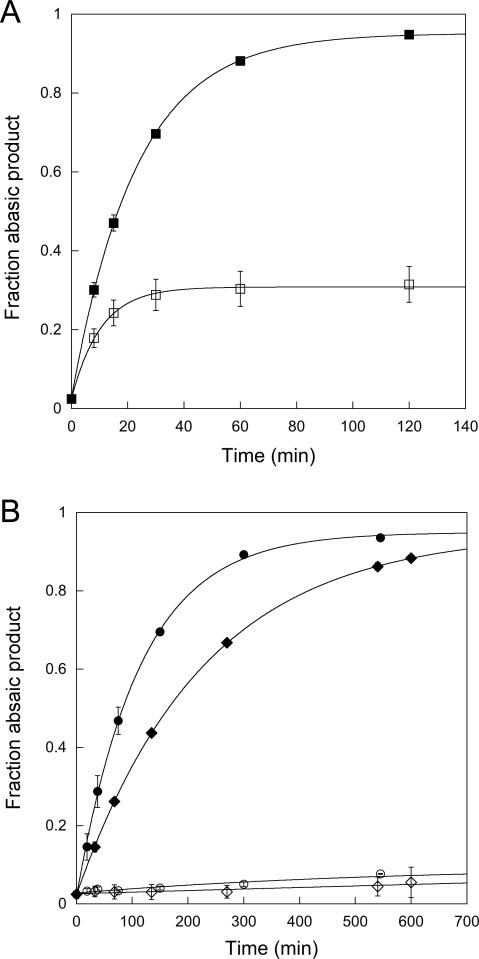
Figure 5.
Pulse-chase experiments to measure dissociation of εA-DNA. The partitioning between the forward reaction (base excision) and substrate dissociation were measured for wildtype, Y127W, and Y159W AAG. Either wildtype (A) or mutant (B) AAG was mixed with fluorescein-labeled εA-DNA in the presence (open symbols) or absence (closed symbols) of excess unlabeled εA-DNA as described in the Materials and Methods. The fraction of fluorescent abasic DNA product was quantified using the standard gel-based glycosylase assay. For the wildtype enzyme approximately 30% of the εA-DNA is committed to excision. In contrast, essentially all of the εA-DNA dissociated from both Y127W (◇) and Y159W (○) mutant proteins under these conditions, indicating the kunflip is much greater than kchem (Scheme 2).