Figure 1.
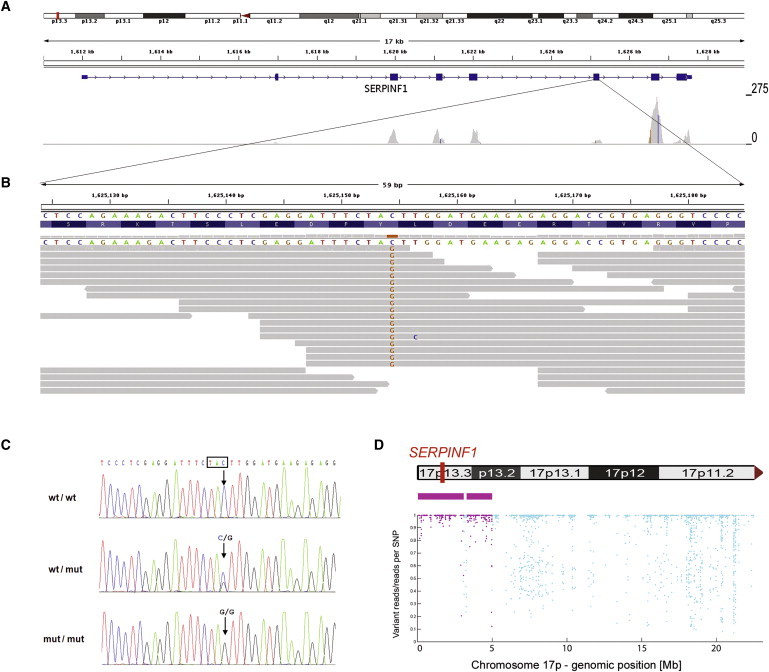
Identification of a Homozygous Mutation in SERPINF1 by Exome Sequencing
(A) Overview of SERPINF1 coverage by exome sequencing. Upper: An ideogram illustrating the SERPINF1 location in the chromosomal band 17p13.3 (red bar). Middle: The genomic structure and localization of SERPINF1 in more detail. Lower: The per-base coverage, with an axis to the right ranging from 0 to 275-fold coverage.
(B) Detailed view of individual sequencing reads overlapping the stop mutation in exon 6. All 18 reads at the genomic position g.1,625,154 (hg18) display the homozygous stop mutation c.696C>G.
(C) Validation of the SERPINF1 mutation in exon 6 by Sanger sequencing of genomic DNA. Electropherograms of a control individual, of the index patient, and of his father are shown. The position of the mutation is marked with an arrow. The affected codon is framed in black. The control individual carries the wild-type sequence (wt) in both copies of the gene. The patient's father is a heterozygous carrier of the mutation (genotype wt/mut). The patient is homozygous for the c.696C>G mutation (mut/mut).
(D) Upper: Contains an ideogram of the p-arm of chromosome 17 illustrating the localization of SERPINF1. Lower : The homozygous regions on chromosome 17 at the genomic positions g.97,058-3,091,589 and g.3,299,188-4,983,922 are recognizable. Each dot represents one of the SNP markers that were included in the analysis. SNPs within a region that was called as homozygous are colored in purple. The position along the y axis indicates the ratio of the number of reads with the nonreference allele to the total number of reads; the value is 1.0 if only reference or nonreference reads are present at a given SNP position (y axis, ratio of variant reads/all reads per SNP position; x axis, genomic position along the p-arm of chromosome 17).
