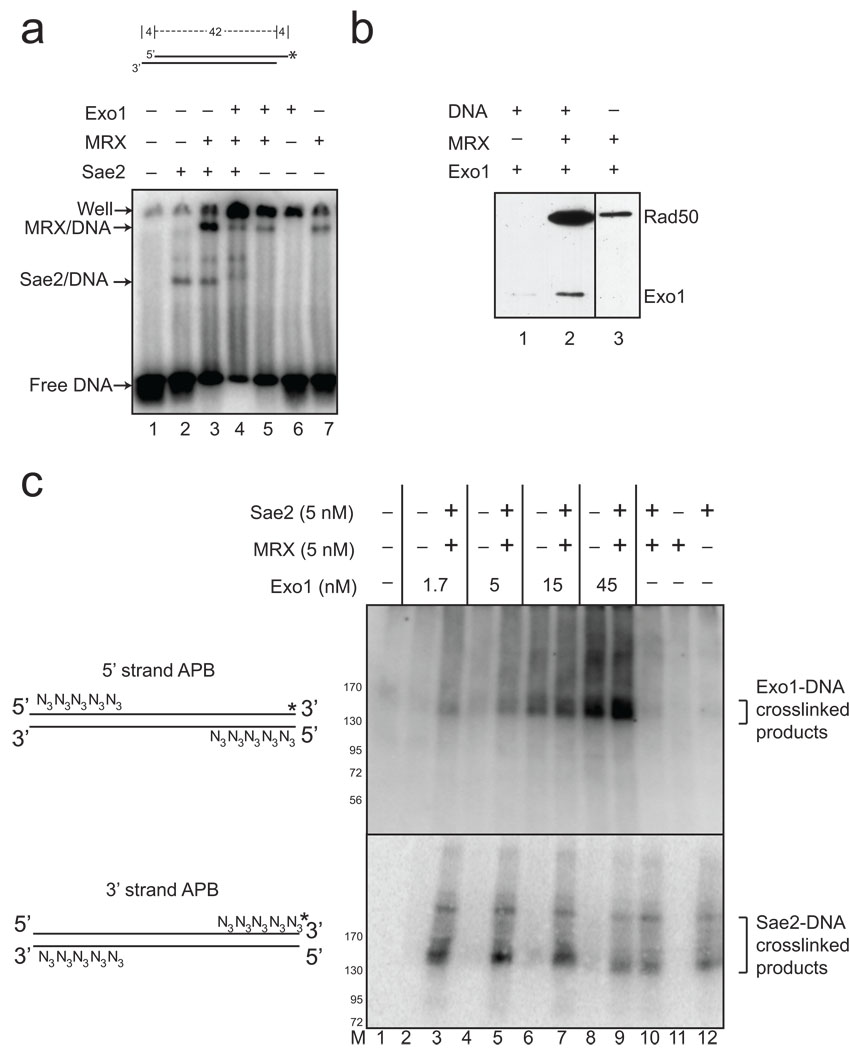
Figure 6. MRX and Sae2 promote Exo1 DNA binding.
(a) Gel mobility shift assays were performed with wild-type MRX (2.5 nM), Sae2 (2.5 nM), and Exo1 D173A (4 nM) proteins as indicated and a 32[P]-labeled, double-stranded oligonucleotide substrate containing 4 nt 3’ overhangs on both ends. Reactions were incubated for 15 min on ice before separation on a native acrylamide gel. (b) MRX and Exo1 D173A proteins were incubated with biotinylated, blunt 100 bp duplex DNA as indicated, crosslinked with formaldehyde, and proteins bound to the DNA were isolated using streptavidin-coated magnetic beads. Bound protein were visualized by SDS-PAGE and western blotting with anti-Flag antibody for Exo1 and Rad50. (c) Protein-DNA binding assays were performed with a 90 bp blunt DNA substrate, containing 5 azide groups (N3) on the 5' ends of the 5' strands or the 3' ends of the 3' strands as shown in the diagram. Both DNA substrates were labeled with 32[P] ("*"). Proteins were incubated with the DNA substrates on ice, UV irradiated, separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane to remove all uncrosslinked DNA before phosphorimager analysis. Migration of molecular weight markers in the gels are shown in the lane marked “M”.