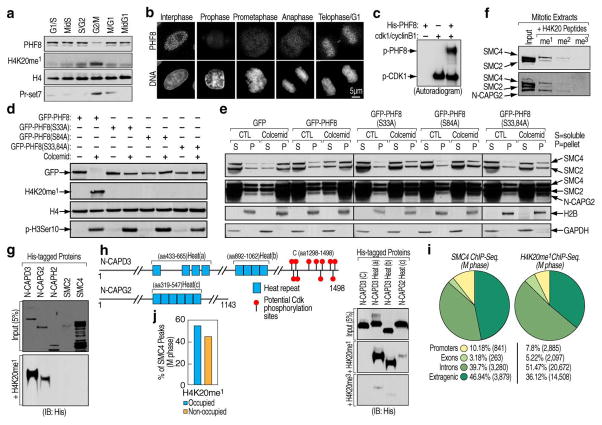
Figure 4. Phosphorylation-dependent PHF8 dissociation from chromatin in prophase links H4K20me1 with Condensin II.
a, Chromatin-bound fractions from HeLa cells synchronized to different cell cycle phases were analyzed by immunoblotting. b, Asynchronously growing HeLa cells were pre-extracted with 0.1% Triton X-100, fixed and stained with PHF8 and Hoechst dye (DNA). Representative images for different cell cycle phases were shown as indicated. Scale bar, 5 μm. c, His-tagged PHF8 phosphorylation by CDK1/cyclinB1 in vitro. d, HeLa cells transfected with GFP-tagged wild type or phosphorylation mutant PHF8 were treated with or without colcemid and chromatin bound fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting. e, HeLa cells transfected with GFP empty vector, wild type or phosphorylation mutant PHF8 in the presence or absence of colcemid were sorted. Chromatin-free (S) and –bound (P) fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting. f, Peptide pull-down assays performed mixing HeLa mitotic extracts with biotinylated histone tails. Pull-downs were analyzed by immunoblotting. g, Peptide pull-down assays performed mixing bacterially-expressed full length proteins with biotinylated histone tail as indicated. Input (upper panel) and pull-downs (bottom panel) were analyzed by immunoblotting. h, Schematic representation of N-CAPD3 and N-CAPG2 proteins27. Peptide pull-down assays were performed by mixing His-tagged C-terminus of N-CAPD3 (lane 1) or HEAT repeat clusters from N-CAPD3 or N-CAPG2 (lane 2–4) with biotinylated histone tails as indicated. Input (upper panel) and pull-downs (bottom two panels) were analyzed by immunoblotting. i, The genomic distribution of SMC4 and H4K20me1 ChIP-Seq peaks in M phase HeLa cells (n=8,263 and 40,162, respectively). j, Bar graph displaying the association of SMC4 and H4K20me1 peaks in M phase HeLa cells.