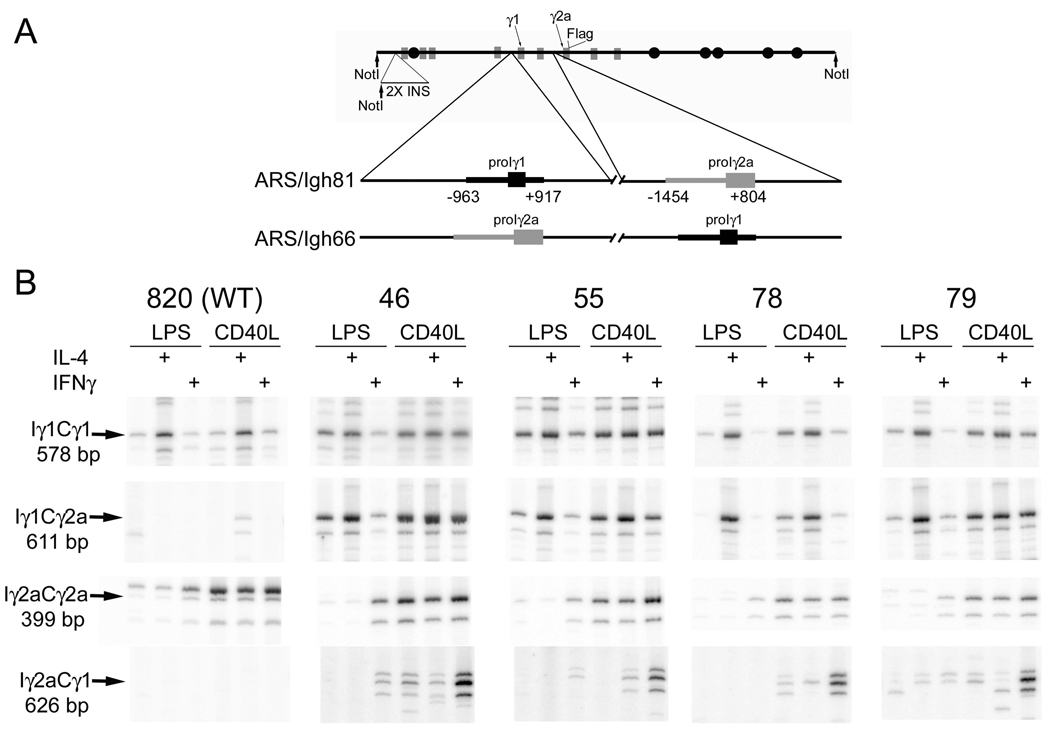
Figure 2.
H chain transgene with a swap of the γ1 promoter/I exon and the γ2a promoter/I exon. A. Structure of the ARS/Igh 66 transgene. Coding regions are depicted as grey boxes and enhancer elements as black circles. A 2.4 kb fragment including two copies of the chicken β-globin insulator (“2X INS”), with an engineered NotI restriction site, was inserted 3 kb 5’ of the VDJ exon. See text for further explanation. B. Expression of chimeric germline transcripts from the ARS/Igh66 transgene. cDNA from B cell culture of the indicated transgenic lines, expression of Iγ1Cγ2a, Iγ2aCγ1 transcripts, γ2a germline transcripts, and γ1 germline transcripts. The chimeric germline transcripts were cloned and sequenced, and found to be the predicted products, with splicing from the major splice site of the Iγ1 or Iγ2a exon to the appropriate CH1 acceptor splice site (20,21). Within each transgenic line, the cDNA were first adjusted to be approximately equal for expression of transgenic VDJCμ transcripts (see Fig. 3). The slower migrating, more intense, band in the line 820 Iγ2aCγ2a panel is the transgenic germline transcripts (403 bp) from the wild type transgene. The second slowest band (399 bp) represents germline transcripts of the endogenous γ2a gene (present in all lanes), and the fastest migrating band is an alternative splice product of the γ2a germline transcripts (21).