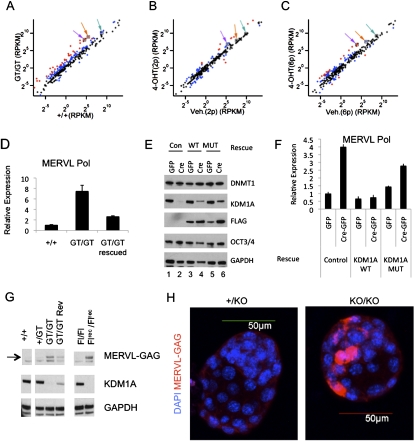
Figure 3.
KDM1A represses MERVL retroviruses in ES cells and preimplantation development. (A–C) mRNA-seq was performed on polyA-enriched mRNAs from Kdm1a +/+ and GT/GT ES cells (A), or Kdm1a FL/FL Cre-ERT ES cells treated with vehicle or 4OHT and passaged two (B) or six (C) additional times. Each plot displays the expression value (in RPKM) of repetitive sequences in wild-type (x-axis) and mutant (Y-axis) ES cells. Data points in red indicate a greater than fourfold difference in the mutants, while those in blue indicate a greater than twofold difference. Colored arrows label the following: MERVL (purple), L1- (orange), and SINE-B2 (green). (D) qRT–PCR analysis was performed on Kdm1a +/+, GT/GT, and GT/GT rescued clones with MERVL Pol-specific primers and plotted relative to Gapdh. (E,F) Kdm1a FL/FL ES cells stably expressing a neo resistance control plasmid (Con; lanes 1,2), Flag-hKDM1A (WT; lanes 3,4), or catalytically inactive Flag-hKDM1A (MUT; lanes 5,6) were transfected with either GFP alone or Cre-GFP as indicated to remove the endogenous mouse Kdm1a alleles. GFP+ cells were collected 24 h later and plated for an additional 48 h before being subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibody (E) or qRT–PCR with MERVL primers and plotted relative to Gapdh (F). Error bars represent SD. (G) Whole-cell extracts from ES cells of the indicated genotype were subjected to immunoblots with the indicated antibodies. (H) Immunofluorescence microscopy using anti-MERVL Gag antibodies (red) was performed on Kdm1a +/KO or KO/KO blastocysts and overlaid with DAPI (blue).