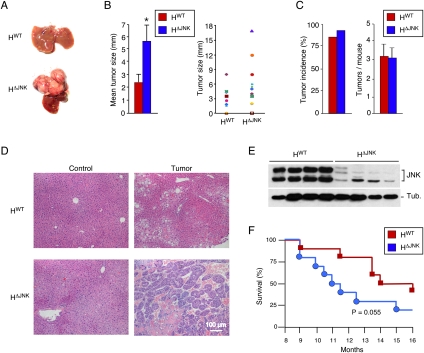
Figure 2.
Effect of hepatocyte-specific JNK deficiency on HCC. (A) DEN-induced HCC in control mice (HWT mice: Alb-Cre+/−) and JNK-deficient mice (HΔJNK mice: Alb-Cre+/− Jnk1LoxP/LoxP Jnk2−/−) at 38 wk of age. (B) The maximum diameter of individual tumor nodules (right panel) and the mean ± SD (n = 13) width of the tumor nodules (left panel) are presented. Statistically significant differences between HWT and HΔJNK mice are indicated. (*) P < 0.05. (C) The tumor incidence (left panel) and the number of tumors per mouse (right panel) were examined (n = 14). No statistically significant differences between HWT and HΔJNK mice were detected. (D) Representative sections of liver from mice treated without DEN (control) and with DEN (tumor) stained with H&E are presented. (E) Immunoblot analysis of tumors isolated from HWT mice and HΔJNK mice was performed by probing with antibodies to JNK and α-Tubulin (Tub.). (F) Kaplan-Meier analysis of the survival of HWT mice and HΔJNK mice (n = 10) treated with DEN is presented. No statistically significant difference between the survival or mortality of HWT mice and HΔJNK mice was detected (log-rank test; P = 0.055).