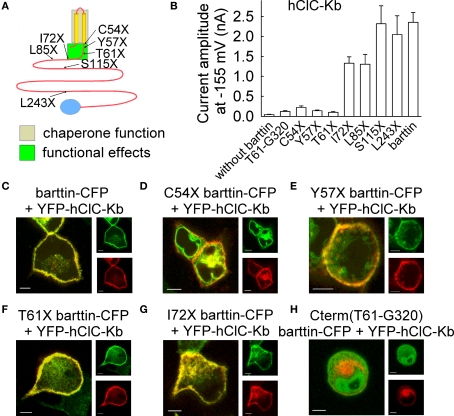
Figure 4.
Truncation mutants of barttin affect subcellular distribution and functional properties of hClC-Kb channels. (A) Localization of tested carboxy-terminal truncations that result in functional deficits of barttin. Chaperone function of barttin is assigned to the two transmembrane domains. (B) Mean isochronal current amplitudes of hClC-Kb determined 2 ms after a voltage step to −155 mV on cells co-expressing WT or various truncated versions of barttin. (C–H) Confocal images of MDCK cells co-expressing YFP-hClC-Kb (red) and various mutants of barttin-CFP (green). Scale bars: 5 μm. (modified from Scholl et al., 2006, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 103, 11411–11416, copyright (2006) National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A).