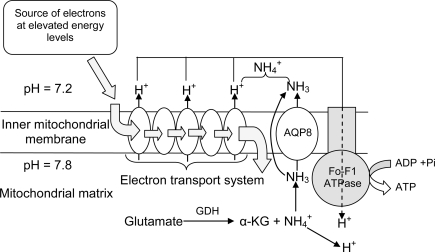
Figure 3.
The catabolism of excess amino acids through transdeamination in the liver mitochondrial matrix releases α-ketoglutarate (αKG) and through the deamination of glutamate catalyzed by glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH). Some would dissociate to NH3 and H+ in the matrix which has a more alkaline pH than the inter-membranous space and the cytosol. The permeation of NH3 through aquaporin channels (e.g., aquaporin 8, APQ8) or the phospholipid bilayer would disrupt the H+ gradient set up by the electron transport system (ETS) across the inner mitochondrial membrane and uncouple ETS from oxidative phosphorylation.