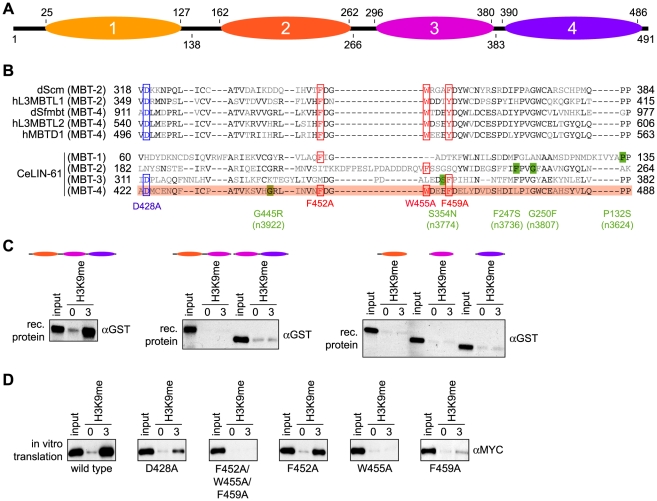
Figure 2. The three C-terminal MBT repeats of LIN-61 are essential for H3K9me3 interaction.
(A) Schematic representation of the LIN-61 protein indicating the amino acid position of the four (1-4) MBT repeat domains on top (according to GenBank using RPS-BLAST). Bottom, boundaries of the deletion constructs used (amino acid positions). (B) Sequence alignment of the four LIN-61 MBT core domains with MBT core domains of other MBT factors implicated in methyl-lysine binding. Amino acids identical in at least three of the sequences are in black. Residues shown to be essential for methyl-lysine interaction of dScm, hL3MBTL1 (isoform I), hL3MBTL2, dSfmbt (isoform C) and hMBTD1 are boxed in red (aromatic cage residues mediating hydrophobic and π-cation interactions) or in blue (conserved aspartate residue mediating ion pairing and hydrogen bonding to mono- and dimethylammonium moiety of lysine ε-amino group). MBT repeat four of LIN-61 containing all residues determined to be essential in methyl-lysine binding of other MBT domain proteins is highlighted in red. Amino acid positions of point mutants generated in this study (red and blue) or corresponding to lin-61 alleles identified in genetic screens (green) are indicated. (C) Affinity purification experiments of bacterially produced recombinant GST-LIN-61 proteins corresponding to the indicated MBT regions using immobilized unmodified and H3K9me3 peptides. αGST Western blot analyses of the recovered material are shown. Input, 2%. (D) Affinity purification experiments of in vitro translated wild type or point mutant MYC-LIN-61 proteins using immobilized unmodified and H3K9me3 peptides. αMYC Western blot analyses of the recovered material are shown. Input, 7.5%.