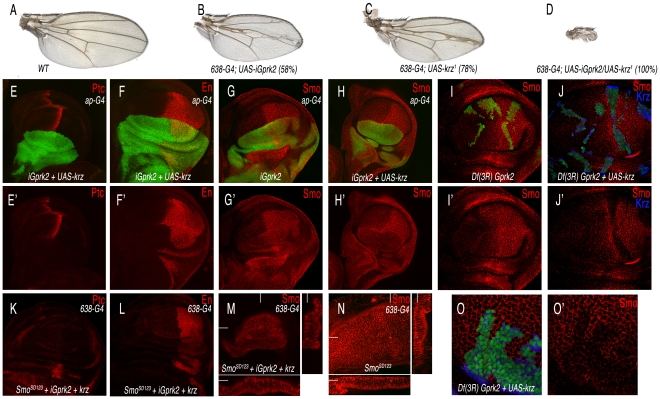
Figure 8. Interactions between Gprk2 and Krz in Smo signalling.
(A) Wild type control wing. (B) Gprk2 loss-of-function phenotype resulting from iGprk2 over-expression in the wing blade (638-Gal4/+; UAS-iGprk2/+). (C) Krz gain-of-function phenotype resulting from UAS-krz over-expression in the wing blade (638-Gal4). (D) Genetic interaction between Gprk2 loss of expression and krz gain of expression. Over-expression of Krz when Gprk2 levels are reduced cause a strong Hh los-of-function (638-Gal4/+; UAS-iGprk2/+; UAS-krz/+). (E–F) Third instar wing discs over-expressing Krz and reducing Gprk2 levels in the dorsal compartment (ap-Gal4 UAS-GFP/+; UAS-iGprk2/+; UAS-krz/+) have a complete loss of Ptc (red in E) and En (red in F) expression in anterior-dorsal cells. E′–F′ correspond to the single red channels showing Ptc (E′) and En (F′) expression. (G–G′) Expression of Smo (in red) in wing discs reducing Gprk2 expression in the dorsal compartment (ap-Gal4/UAS-GFP; UAS-iGprk2/+; GFP in green). (H–H′) Expression of Smo (in red) in wing discs over-expressing Krz and reducing Gprk2 levels in the dorsal compartment (ap-Gal4 UAS-GFP/+; UAS-iGprk2/+; UAS-krz/+). Note the difference in Smo expression between G′ and H′. (I–J and O) Expression of Smo in third instar wing discs bearing clones of cells homozygous for the Gprk2 deficiency (I–I′) and for the Gprk2 deficiency in cells that also over-express Krz (J–J′). Panels O–O′ correspond to the same genotype as J–J′ at higher magnification. Clones were induced in hsFLP1.22 actin-Gal4 UAS-GFP/+; FRT82 Df(3R)Gprk2/FRT82 tub-Gal80 (I–I′) and in hsFLP1.22 actin-Gal4 UAS-GFP/+; FRT82 Df(3R)Gprk2/FRT82 tub-Gal80; UAS-krz/+ (J–J′ and O–O′). (K–M) Expression of Ptc (K), En (L) and Smo (M) in wing imaginal disc over- expressing an active form of Smo (SmoSD123) and Krz and reducing Gprk2 expression in the wing blade (638-Gal4/SmoSD123; UAS-iGprk2/+; UAS-krz/+). (N) Expression of Smo in wing imaginal disc over-expressing an active form of Smo (SmoSD123) in the wing blade (638-Gal4). Note the reduction in Smo levels in M compared to N. Below are transversal sections and to the right longitudinal sections showing Smo expression.