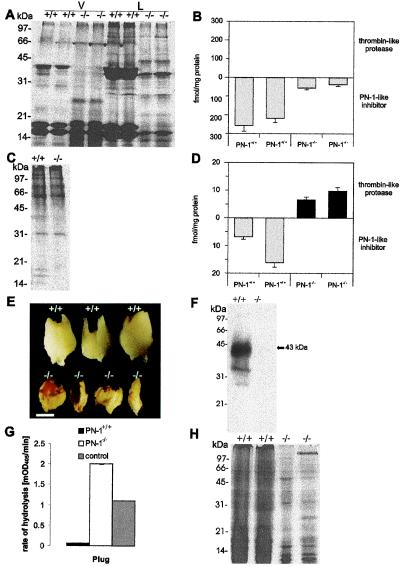
Figure 2.
Biochemical phenotypes in the accessory sex glands and plug formed by PN-1+/+ and PN-1−/− males. (A and C) PAGE of seminal vesicle-secreted proteins and coagulating gland-secreted proteins from adult PN-1+/+ and PN-1−/− mice. The collected seminal vesicle fluid was separated by centrifugation into a liquid (L) and a viscous (V) fraction. Wild-type seminal liquid phase revealed three major bands, with estimated molecular masses of 38, 17, and 16 kDa (A). In the corresponding PN-1−/− samples, the 38-kDa component was strongly decreased and a component of around 28 kDa was observed. The same general pattern was found in the viscous fraction, but in this case other bands of intermediate size were seen in the mutant samples (A). There was no difference in the coagulating gland protein patterns of PN-1+/+ and PN-1−/− mice (C). (B and D) Amount of thrombin-like protease and PN-1-like inhibitor in the seminal vesicle and the coagulating gland of 14-day-old PN-1+/+ and PN-1−/− mice. In the mutant mice, seminal fluid showed reduced thrombin inhibitory activity (B), whereas coagulating gland fluid showed an excess of unidentified thrombin-like protease activity (D). Notice the different scales used in B and D. (E) A decrease in plug size as well as a modified appearance is clearly seen in PN-1−/− mice compared with the plug generated by wild type. Plugs are oriented with their proximal ends at the top. (Scale bar, 0.75 mm.) (F) Immunoblot indicates that PN-1 is secreted during ejaculation and is then present in plugs generated by PN-1+/+ males. (G) Proteolytic activity assay in plugs homogenates in the presence of added thrombin. The surplus proteolytic activity detected in plugs generated by PN-1−/− males compared with the buffer control with 0.1 nM added thrombin (see Materials and Methods) indicates an endogenous PN-1-sensitive proteolytic activity. (H) Coomassie blue staining of PAGE-analyzed proteins contained in plugs generated by PN-1+/+ and PN-1−/− mice. Each lane was loaded with 5 μg protein.