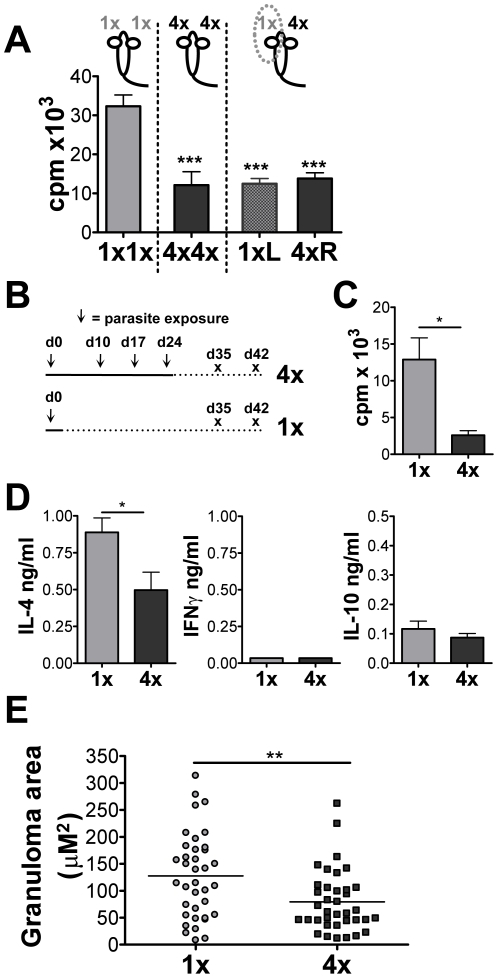
Figure 2. Multiple infections cause systemic immune hypo-responsiveness and down-regulate the size of egg-induced granulomas in the liver.
(A) Antigen-specific proliferation of sdLN cells from pinnae exposed to 1x or 4x infections on the left pinnae (1xL) or right pinnae (4xR), or both (1x1x and 4x4x). Results show mean 3H-thymidine incorporation (c.p.m.) + SEM (n = 5 mice). (B) Infection regime used to assess the effect of repeated infection on the immune response to mature parasites. (C) Egg-antigen specific proliferation of mesenteric LN cells taken on day 35 from 1x and 4x mice. Bars shows mean 3H-thymidine incorporation (c.p.m.) + SEM (n = 5 mice). (D) Egg antigen-specific IL-4, IFNγ and IL-10 production by mesenteric LN cells taken on day 42 from 1x and 4x mice. Bars shows mean cytokine production + SEM (n = 4 mice). (E) Size of hepatic granulomas surrounding single eggs in 1x and 4x mice on day 42; Points are granuloma areas (measured as µm2 from H&E stained liver sections + SEM; n = 37 granulomas). P values are of 4x mice compared to 1x mice.