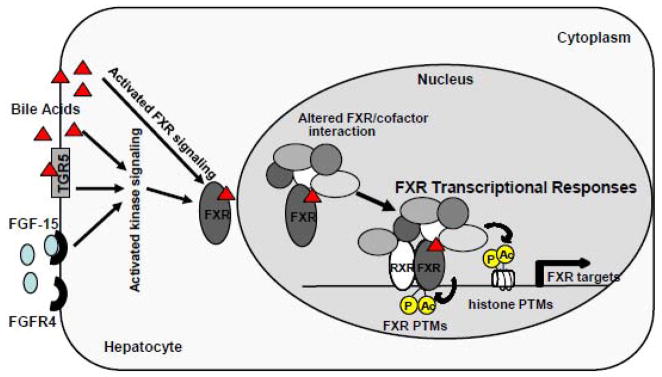
Fig. 1. FXR transcriptional responses by PTMs and cofactor interaction in response to bile acid signaling.
Bile acids activate cellular kinases (JNK, ERK, PKB, PKC), nuclear receptors, primarily FXR, and a membrane GPCR TGR5. Intestinal FGF-15 (FGF-15 is the mouse homologue of human FGF-19), upon induction by bile acid-activated FXR, binds to a liver membrane receptor tyrosine kinase, FGFR4, and triggers cellular kinase signaling cascades in hepatocytes. In response to these multiple bile acid-activated cellular signaling pathways, interaction of FXR with transcriptional cofactors is changed, which results in altered PTMs of FXR as well as histones to effectively modulate expression at target genes.