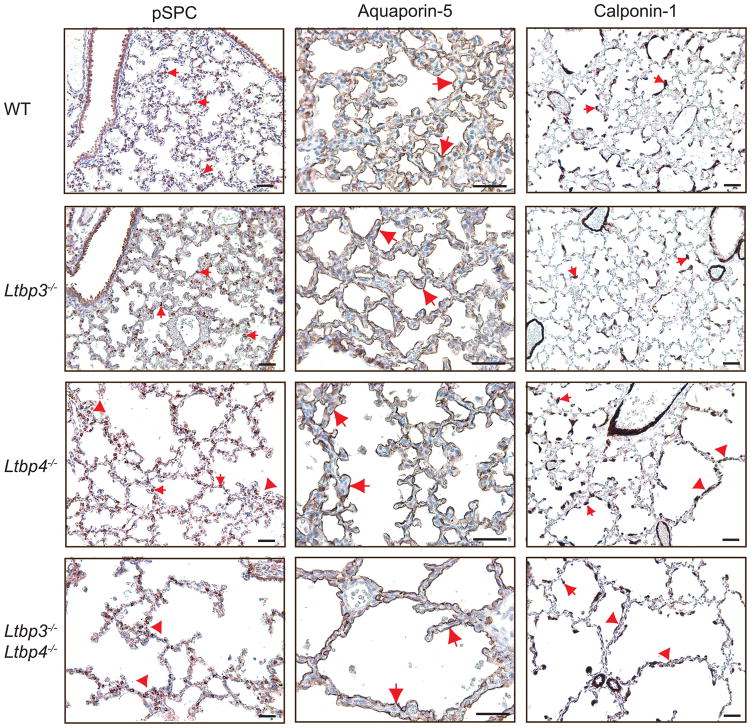
Figure 6.
Differentiation of Type 1 and 2 epithelial cells and myofibroblasts in Ltbp3−/−, Ltbp4S−/− and Ltbp3−/−;Ltbp4S−/−. Left. Type 2 cells were stained with an antibody against proSP-C. The differentiation and distribution of Type 2 cells (arrows) appear normal in WT and Ltbp3−/−lungs, whereas abnormally large clusters (arrowheads), and areas with decreased number of Type 2 cells were observed in Ltbp3−/−;Ltbp4S−/− lungs, and in the large-air sac areas in Ltbp4S−/−lungs. Center. Type 1 cells were stained with an antibody against Aquaporin-5. Aquaporin-5 is detected at the alveolar surface of all four genotypes (arrows), indicating Type-1 cell maturation in Ltbp3−/−, Ltbp4S−/− and Ltbp3−/−;Ltbp4S−/− lungs. Right. SMCs and myofibroblasts (arrows) were stained with an antibody against calponin-1. In WT, Ltbp3−/− and in the areas of small, i.e. normal air sacs in Ltbp4S−/− lung parenchyma myofibroblasts (arrows) are localized on the tips of septating air sacs and in airway walls. In the areas with arrested septation in Ltbp4S−/−, as well as in Ltbp3−/−;Ltbp4S−/− lungs there was an increase in myofibroblast numbers in abnormal septae of large air sacs (arrowheads). Bars: 40 μm.