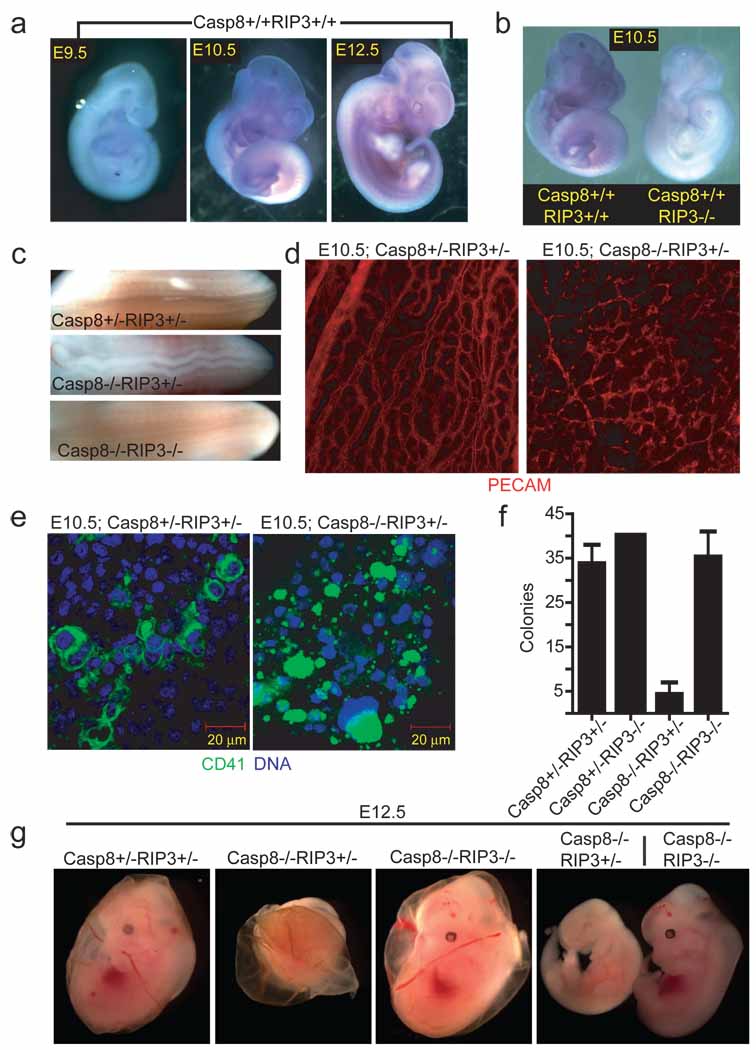
Figure 1.
Embryonic expression of Rip3. (a) Whole-mount Rip3 in situ hybridization of Casp8+/+Rip3+/+ E9.5 (left panel), E10.5 (middle panel), and E12.5 (right panel) embryos. (b) Whole-mount Rip3 in situ hybridization of Casp8+/+Rip3+/+ and Casp8+/+Rip3−/− E10.5 embryos demonstrating specificity of the probe. (c) View of the neural tube of E11.5 embryos with the indicated genotype. (d) PECAM-1 (CD31) staining of a whole-mount E10.5 yolk sac from a representative Casp8+/−Rip3+/− (left panel) and Casp8−/−Rip3+/− (right panel) embryo (100X). (e) CD41 (green) and nuclear DNA (blue) staining of a yolk sac from a E10.5 Casp8+/−Rip3+/− (left panel) and a Casp8−/−Rip3+/− (right panel) embryo. (f) Numbers of colony-forming cells (CFC) following culture of disrupted E10.5 yolk sacs of the indicated genotype. (g) Photographs of E12.5 embryos and yolk sacs with the indicated genotype. The right panel shows side by side embryos with yolk sacs removed.