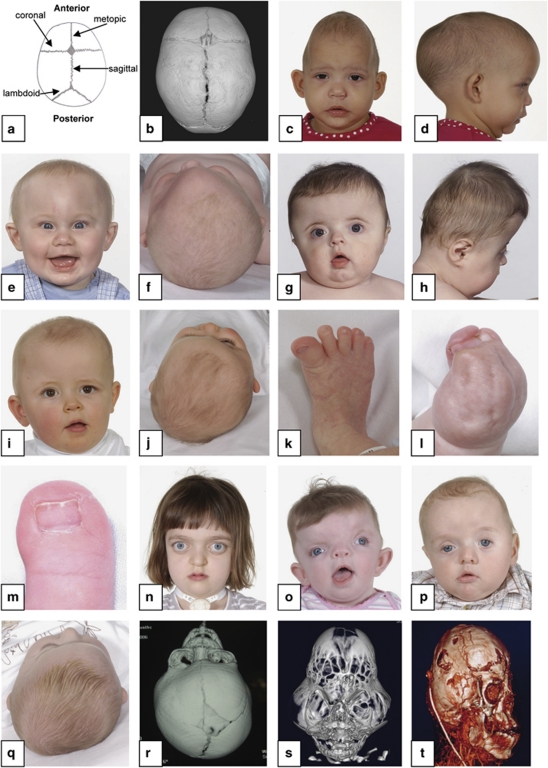
Figure 1.
Diagnostic features of craniosynostosis. (a) Schematic diagram showing positions of the major cranial sutures. (b) CT scan (vertex view of skull) showing major sutures; anterior is at top. (c,d) Sagittal synostosis: note long, narrow head. (e,f) Metopic synostosis: note hypotelorism and triangular profile of forehead. (g,h) Bicoronal synostosis: broad, flattened head. (i,j) Right unicoronal synostosis: note flattened brow and anterior position of ear on affected side, deviation of nasal tip and prominent brow on unaffected side. (k–m), Congenital anomalies of feet or hands characteristic of Pfeiffer syndrome (k), Apert syndrome (l) and craniofrontonasal syndrome (m). (n) Crouzonoid facial appearance. (o) Severe hypertelorism, grooved nasal tip and left unicoronal synostosis in craniofrontonasal syndrome. (p) Ptosis and left unicoronal synostosis in Saethre-Chotzen syndrome. (q) Positional plagiocephaly: prominence on right anteriorly and left posteriorly, with right ear anterior and parallelogram shape to skull. (r) CT reconstruction showing left unicoronal synostosis. (s) CT reconstruction showing cloverleaf skull. (t) CT venogram showing abnormal venous drainage in multisuture syndromic craniosynostosis. See text for further details.