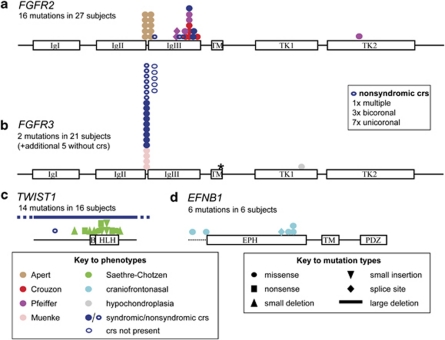
Figure 2.
Distribution and types of mutation that commonly cause craniosynostosis. The major domains of the proteins encoded by the FGFR2 (a), FGFR3 (b), TWIST1 (c) and EFNB1 (d) genes are shown to scale, together with the position and types of mutation identified, and their associated phenotypes. Dashed line before EPH domain encoded by EFNB1 indicates 5′ untranslated region. The data, which were obtained from the Oxford cohort study,7 convey the relative prevalence of the most common mutations, but many rare mutations were absent in this survey. Asterisk indicates position of Ala391Glu mutation of FGFR3. crs, craniosynostosis. See text for information on protein domains.