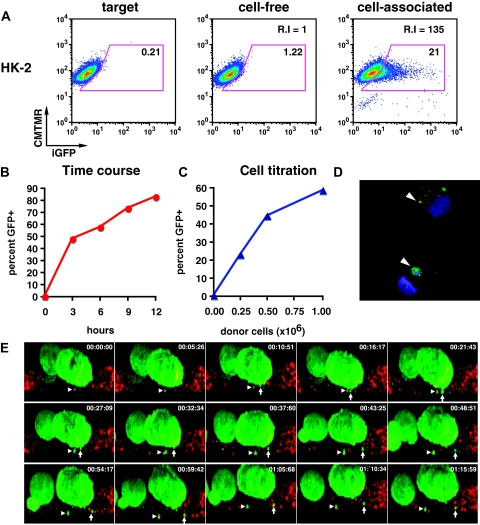
Figure 3.
Cell-associated virus acquisition by renal tubular epithelial cells is more efficient than cell-free viral uptake. (A) HK-2 cells before (left) and after exposure to cell-free HIV Gag-iGFP (middle) or cell-associated HIV Gag-iGFP (right). (B) Time course of T cell to HK-2 cell viral transfer at 3, 6, 9, and 12 hours of co-culture. (C) Titration of donor cells (0, 0.25 × 106, 0.5 × 106, and 1 × 106) resulted in a dose-dependent transfer of fluorescence. (D) Confocal images of flow-sorted HK-2 cells after virus transfer. DAPI staining of nuclei (blue); HIV Gag-iGFP (green); arrowhead, GFP-positive viral material. (E) Live imaging of viral transfer from HIV Gag-iGFP expressing Jurkat (green) to HK-2 (CMTMR-labeled, red). Selected XZ-projection from time lapse images for about 1 hour and 15 minutes. Arrow and arrowhead indicate two viral puncta emerging from donor cell and entry into target cells.