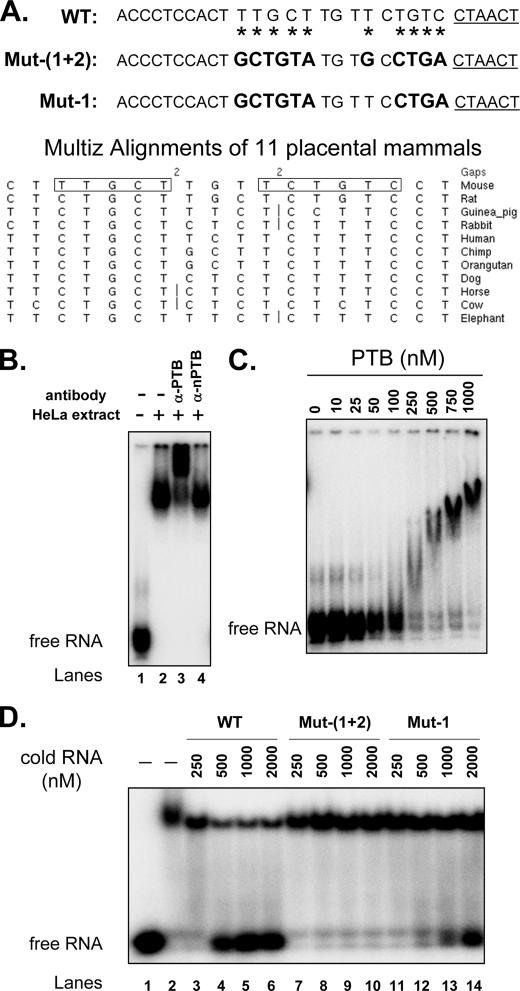
FIGURE 4.
PTB binds specifically to sequences upstream of exon 8a. A, upper panel, RNA probes containing the wild-type sequence upstream of the putative exon 8a branch point (underlined) or mutant sequences as indicated. Mutated nucleotides are indicated by asterisks on the wild-type probe and are highlighted in boldface on the mutant RNA probes. Lower panel, alignment (UCSC Genome Browser) of placental mammal intron sequence affecting the regulation of exon 8a by PTB. The boxed sequences are those mutated in the upper panel. B, EMSA of PTB binding to the wild-type probe in HeLa extract. In vitro transcribed labeled RNA probe was incubated in binding buffer (lane 1) or HeLa nuclear extract (lane 2) or in HeLa nuclear extract followed by the addition of anti-PTB (lane 3) or anti-nPTB (lane 4) antibody. C, EMSA of purified PTB binding to the sequence upstream of exon 8a. The wild-type probe was incubated in binding buffer containing increasing concentrations of His-PTB protein, as indicated. D, the pyrimidine-rich elements upstream of exon 8a specifically compete for PTB binding. Lane 1, EMSA of labeled wild-type RNA (25 nm) not incubated with PTB; lanes 2–14, EMSA of labeled wild-type RNA (25 nm) preincubated with purified PTB (1000 nm) and unlabeled wild-type or mutant RNA probes at the concentrations indicated. Note that mutation of the upstream elements drastically reduced the ability of the RNA probe to compete with the wild-type probe for PTB binding.