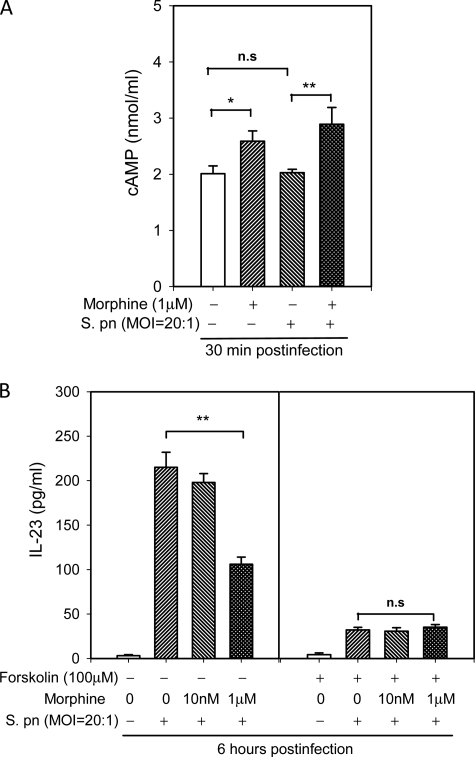
FIGURE 7.
Role of cAMP in the regulation of IL-23 production by morphine in DCs following S. poneumoniae infection. A, morphine treatment resulted in an increase in intracellular cAMP. BMDCs were treated with morphine or vehicle for 24 h and then infected with S. pneumoniae (S. pn) for 30 min. The levels of intracellular cAMP were determined by competitive enzyme immunoassay. B, forskolin inhibited IL-23 synthesis, and the effect of morphine was abolished by pretreatment with forskolin. BMDCs were preincubated with forskolin (100 μm) or vehicle 30 min before cell infection with S. pneumoniae. The data shown are the mean ± S.E. of three experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 comparisons as indicated by brackets. n.s., not significant.