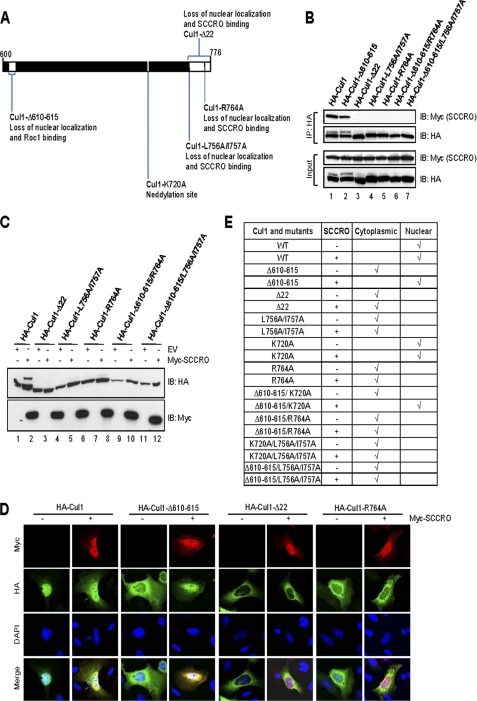
FIGURE 4.
Binding to SCCRO is required for neddylation and nuclear localization of Cul1. A, schematic representation of the C terminus of Cul1 showing cullin mutants used in these experiments. B, immunoblot on lysates from U2OS cells transfected with Myc-SCCRO and HA-Cul1 or selected mutants probed with the indicated antibodies following HA immunoprecipitation. SCCRO binds to HA-Cul1 and HA-Cul1-Δ610–615 (lanes 1 and 2) but not C-terminal Cul1 mutants (lane 3–7). C, immunoblots for Cul1 on lysates from U2OS cells co-transfected with Cul1 or its mutants with or without SCCRO showing mutants that lose SCCRO binding cannot be neddylated. D, immunofluorescence using Cy3-conjugated anti-Myc antibody and FITC-conjugated anti-HA antibody on U2OS cells transfected with HA-Cul1 or indicated HA-tagged Cul1 mutants with or without Myc-SCCRO. HA-Cul1 (first lane) was primarily nuclear (∼74%) whereas Cul1 mutants (third, fifth, and seventh lanes) were primarily cytoplasmic in the absence of SCCRO expression. Co-expression of SCCRO increased the proportion of HA-Cul1 and rescued the localization defect of Cul1-Δ610–615 with primary nuclear localization. E, U2OS cells were transfected with Cul1 or its mutants with or without SCCRO. The results of Cul1 localization monitored by immunofluorescence by counting 200 cells for each transfection is tabulated. Nuclear localization by SCCRO requires the Cul1 C-terminal sequence.