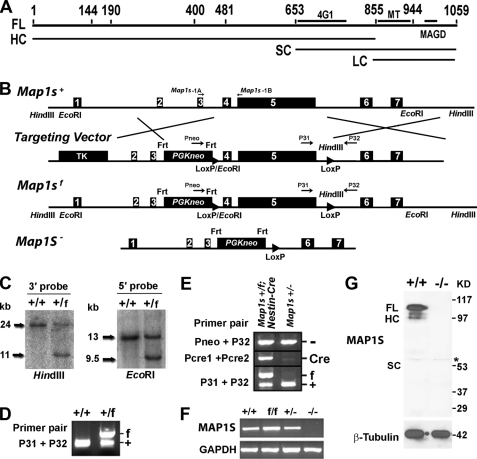
FIGURE 1.
Generation of the Map1s−/− mouse. A, post-translational isoforms of MAP1S are shown. Numbers indicate amino acid residues. FL, 1059-residue full-length translation product; HC, heavy chain; SC, short chain; LC, light chain; 4G1, epitope of the 4G1 antibody; MT, microtubule binding domain; MAGD, mitochondria aggregation and genome destruction domain. B, a schematic of the wild-type mouse Map1s gene (Map1s+), the engineered gene targeting vector, the floxed allele (Map1sf), and the null allele (Map1s−) is shown. Boxed numbers represent the seven exons of the Map1s gene. HindIII and EcoRI restriction enzyme sites are indicated. The indicated TK and PGKneo cassettes carry thymidine kinase and neomycin resistance genes for negative and positive selection, respectively. Frt and LoxP are the target sequences for Flippase or Cre enzymes, respectively. C19-1A, C19-1B, Pneo, P31, and P32 refer to primers for PCR genotyping (supplemental Table 1). C, Southern blot confirmation of Map1sf alleles in ES cells is shown. Genomic DNA from ES clones with wild-type (+/+) and flox allele (+/f) was digested with EcoRI or HindIII and hybridized with the 5′ or 3′ probe, respectively. D, confirmation of Map1sf allele in the mouse genome is shown. E, confirmation of the presence of Map1s− allele in the Nestin-Cre transgenic mice is shown. F, the expression levels of Map1s mRNA in the brains of mice with different genotypes are shown. The mRNA was assessed by RT-PCR with primers C19-1A and C19-1B. G, the expression levels of MAP1S in hearts of mice with different genotypes are shown. MAP1S was assessed by immunoblot with antibody 4G1. The asterisk represents a nonspecific band caused by contaminating mouse antibodies from blood that cross-react with anti-mouse secondary antibody.