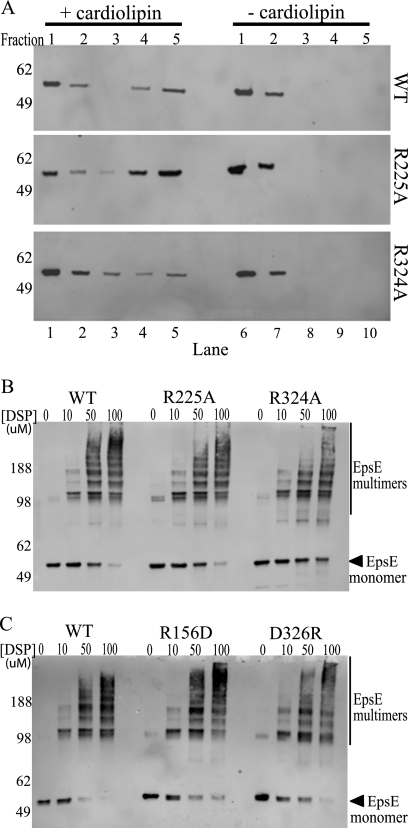
FIGURE 5.
EpsE point mutants interact with cardiolipin and can form oligomers. A, protein-cardiolipin interactions were compared using a liposome floatation assay. Reaction mixtures containing wild type, R225A, or R324A protein ± cardiolipin were subjected to membrane floatation. After centrifugation, five 1-ml fractions were collected and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-EpsE. Molecular mass markers are indicated on the left, fraction numbers are listed across the top, and lane numbers are listed across the bottom. Lanes 4 and 5 are the top fractions in the cardiolipin (+) samples and represent liposome-bound protein, whereas lanes 9 and 10 represent the highest fractions of the cardiolipin (−) samples. B, reactions containing either wild type EpsE-EpsL(1–253)His6 or the point mutants EpsE-R225A or EpsE-R324A protein were cross-linked in the presence of Mg-ATP and cardiolipin using increasing concentrations of DSP (0, 10, 50, or 100 μm). Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-EpsE. Molecular mass markers are denoted on the left, and the position of monomeric EpsE is indicated with an arrow. C, reactions containing either wild type EpsE-EpsL(1–253)His6 or the point mutant EpsE-R156D or EpsE-D326R proteins were cross-linked in the presence of Mg-ATP and cardiolipin as described in B. Molecular mass markers are denoted on the left, and the position of monomeric EpsE is indicated with an arrow.