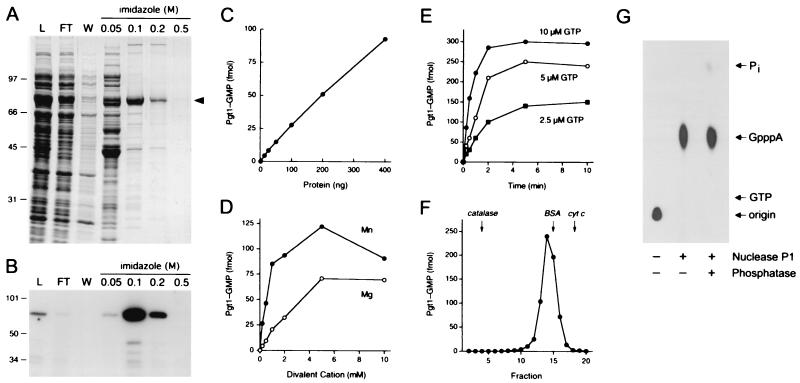
Figure 3.
Characterization of P. falciparum RNA guanylyltransferase. (A) Pgt1 purification. Aliquots (15 μl) of the soluble bacterial lysate (L), the Ni-agarose flow-through (FT), wash (W), and indicated imidazole eluates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. The fixed gel was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue dye. The positions and sizes (in kDa) of marker polypeptides are shown on the left. The Pgt1 protein is indicated by the arrowhead on the right. (B) Guanylyltransferase activity. Reaction mixtures contained 5 mM MgCl2, 0.17 μM [α-32P]GTP, and 1 μl of the protein fractions specified above the lanes. (C) Enzyme titration. Reaction mixtures contained 5 mM MgCl2, 0.17 μM [α-32P]GTP, and Pgt1 as specified. (D) Divalent cation requirement. Reaction mixtures contained 0.17 μM [α-32P]GTP, 200 ng of Pgt1, and either MgCl2 or MnCl2 as specified. (E) Kinetics. Reaction mixtures (100 μl) containing 50 mM Tris⋅HCl (pH 8.0), 5 mM DTT, 5 mM MnCl2, 1 μg of Pgt1, and 2.5, 5, or 10 μM [α-32P]GTP were incubated at 30°C. Aliquots (10 μl) were withdrawn at the times indicated and quenched immediately with SDS. (F) Sedimentation of Pgt1 in a glycerol gradient. The guanylyltransferase activity profile is shown. The peaks of the internal marker proteins are indicated by arrows. (G) RNA cap formation. The RNA reaction product was analyzed by TLC before and after digestion with nuclease P1 and alkaline phosphatase. The positions of the chromatographic origin, GpppA, GTP, and Pi are indicated on the right.