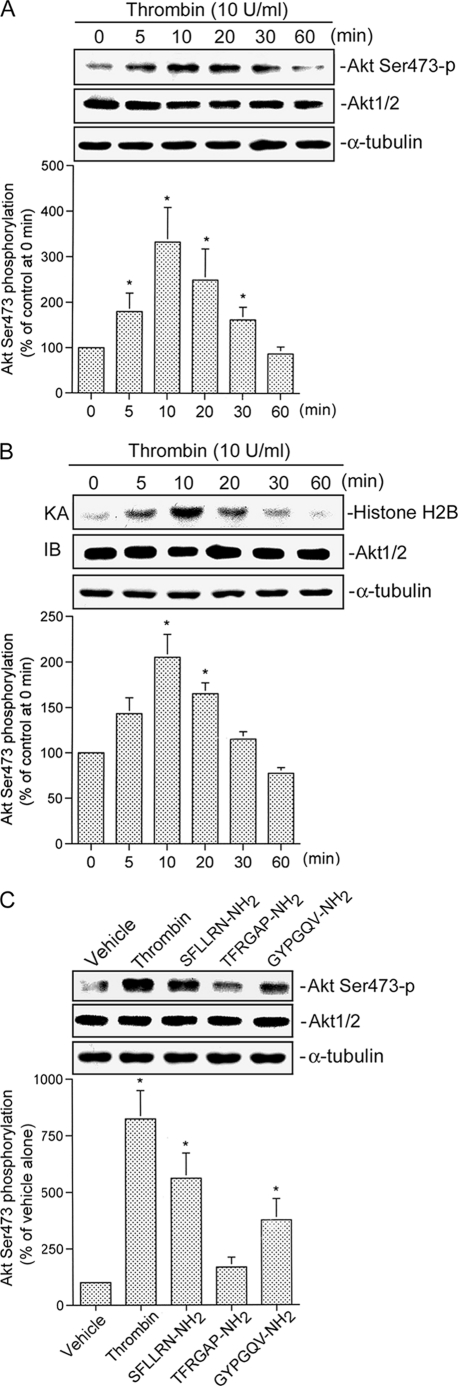
FIGURE 3.
Akt activation is caused by thrombin, a PAR1 agonist, and a PAR4 agonist in A549 cells. A, cells were incubated with 10 units/ml thrombin for the indicated time intervals. Cell lysates were prepared, and then immunoblotted with antibodies for phospho-Akt, Akt1/2, or α-tubulin. Ser473-p, phosphorylated Ser-473. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E. of three experiments performed in duplicate. *, p < 0.05, as compared with the control (0-min time point) group. B, A549 cells were incubated with 10 units/ml thrombin for 0–60 min, and cell lysates were then immunoprecipitated with antibodies specific for Akt1/2. One set of immunoprecipitates was subjected to the kinase assay (KA) described under “Experimental Procedures” using the histone H2B as a substrate. The other set of immunoprecipitates was subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with the anti-Akt1/2 antibody. Equal amounts of the immunoprecipitated kinase complex present in each kinase assay were confirmed by immunoblotting for Akt1/2. α-Tubulin protein in total cell lysates served as the loading control. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E. of three experiments performed in duplicate. *, p < 0.05, as compared with the control (0 min time point) group. C, cells were incubated with an equivalent vehicle control (double-distilled H2O), 10 units/ml thrombin, 300 μm SFLLRN-NH2, 300 μm TFRGAP-NH2, and 300 μm GYPGQV-NH2 for 30 min, and then Akt phosphorylation, Akt1/2, and α-tubulin protein levels were determined. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E. of three experiments performed in duplicate. *, p < 0.05, as compared with the vehicle group.