FIGURE 1.
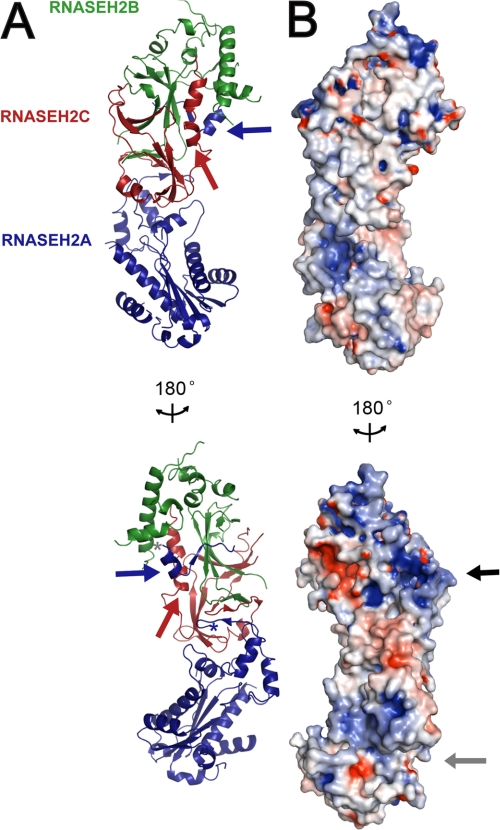
Crystal structure of the heterotrimeric RNase H2 complex. A, ribbon diagram representation of human RNase H2 reveals a linear arrangement of subunits where the core of the catalytic domain (RNASEH2A; blue) is stacked on the interwoven auxiliary RNASEH2B (green) and RNASEH2C (red) subunits. The C terminus of RNASEH2A, residues 284–299 (blue arrow), extends from the core domain and bridges the other two subunits. The first residue of the extension, RNASEH2A:284, and the last residue of the core domain, RNASEH2A:257, are indicated by gray and blue asterisks, respectively. The C terminus of RNASEH2C (red arrow) forms a kinked α-helix at the intersubunit interface. B, electrostatic surface of human RNase H2 indicates two positively charged patches: one in the catalytic active site groove (gray arrow) and the second on the interwoven RNASEH2BC heterodimer (black arrow). Electrostatic surface potential was calculated using PDB2PQR (34) and colored by potential (+9kT/e to −9 kT/e; electropositive in blue and electronegative in red) on the solvent accessible surface using the APBS tool (35). These and all other molecular graphics were generated using PyMOL (DeLano Scientific LLC).