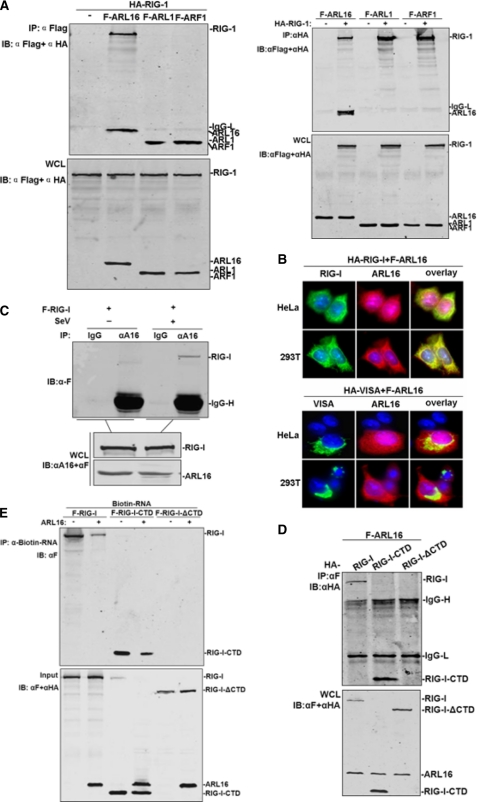
FIGURE 4.
ARL16 associates with the CTD of RIG-I. A, ARL16 but not ARF1 and ARL1 interacts with RIG-I. 293T cells (1 × 106) were transfected with indicated plasmid (5 μg each). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Flag (αF) or anti-HA (αHA). The immunoprecipitates and whole-cell lysates (WCL) were analyzed by Western blot (IB) with anti-HA and anti-Flag antibody. B, ARL16 colocalizes with RIG-I but not VISA in 293T and HeLa cells. Upper panels: HeLa cells were transfected with Flag-ARL16, HA-RIG-I, or HA-VISA. Immunofluorescent staining was performed with anti-HA (green) and anti-Flag (red); lower panels: 293T cells were transfected and stained as in the upper panels. The experiments were repeated twice, and similar results were obtained. C, endogenous ARL16 interacts with RIG-I upon SV infection. 293T (3 × 106) cells were treated with SV or left untreated for 12 h before lysis. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated for Western blot by indicated antibodies. D, identification of domains of RIG-I mediating the interaction with ARL16. 293T cells (1 × 106) were transfected with expression plasmids for Flag-ARL16, together with HA-RIG-I or its mutants (5 μg each). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with indicated antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blots with anti-HA or anti-Flag antibody. E, ARL16 decreases the binding of RIG-I or CTD with RNA. The lysates of cells transfected with Flag-RIG-I, RIG-I-CTD, or RIG-I-ΔCTD were incubated with biotinylated 5′pppRNA transcripts. RNA-protein complexes were pulled down using streptavidin affinity beads. Input and pull-down samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using anti-Flag antibody (one representative of three experiments is shown).