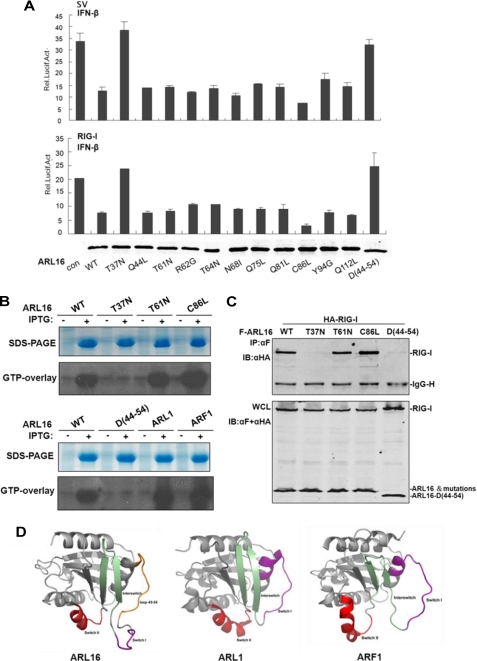
FIGURE 5.
ARL16 functions in a GTP-dependent manner. A, Thr-37 is the essential site for ARL16 inhibitory function. 293T cells (2 × 105) were transfected with the IFNβ reporter plasmid (50 ng) and pRL-TK Renilla luciferase plasmid (50 ng), together with an empty vector and ARL16 wild type and mutations (100 ng each). Cells were infected with SV for 12 h or cotransfected with plasmid for RIG-I (100 ng). Lower panel: expression of RIG-I wild type (WT) and mutations. B, T37N lost GTP binding activity. Bacterial cells were transformed with indicated expression constructs and induced with IPTG or left untreated. Total cellar proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose filters and after renaturation allowed to bind [α-32P]GTP. Bound [α-32P]GTP was visualized by autoradiography. Upper panels: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie brilliant blue to assess protein concentration. C, T37N and deletion-45–54 mutants do not interact with RIG-I. 293T cells (1 × 106) were transfected with expression plasmids for Flag-ARL16 wild-type or mutations with HA-RIG-I (5 μg each). Immunoprecipitation and Western blot were performed as in Fig. 4A. D, three-dimensional models of ARL16 (left), ARL1 (middle), and ARF1 (right) shown as cartoons by the program Pymol. Switch I, Interswitch, and Switch II are indicated in purple, green, and red, respectively. The excess loop 45–54 in the three-dimensional model of ARL16 is colored orange.