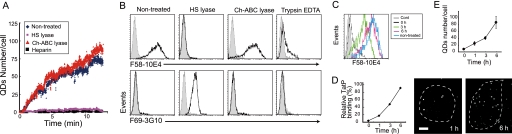
FIGURE 5.
HSPGs are essential for initial TatP cell-surface binding. A, typical time course of monovalent TatP-QD cell binding to HeLa cells treated with 20 milliunits of HS lyase or 0.5 units of Ch-ABC lyase or cultured with 10 units of heparin. Images were collected at 400 ms/frame. B, binding of a mAb specific for intact HSPGs (F58-10E4) or for an epitope generated by the cleavage of HSPGs with HS lyase (F69-3G10). Cells were treated with 20 milliunits of HS lyase (middle right panel), 0.5 units of Ch-ABC lyase (middle left panel), or 0.5% trypsin/EDTA (right panel); nontreated cells (left panels) were stained with the indicated Abs and analyzed by FACS. Dark lines represent anti-HSPG Abs; light lines represent isotype-control. C, turnover of HSPG (F58-10E4) in cells treated with 0.5% trypsin/EDTA by FACS. D, recovery of the cell-surface binding capability of 8-val TatP-QDs in cells treated with 0.5% trypsin/EDTA. Data were calculated from the MFI values by FACS. E, recovery of the cell-surface binding capability of 8-val TatP calculated from single particle images of 8-val-TatP binding in cells treated with 0.5% trypsin/EDTA. The relative binding capability of 8-val TatP over time was calculated from the mean numbers of TatPs/cell based on 20 observed cells (upper graph) and selected images (lower panels). Bars, S.D. Results are representative of three independent experiments.