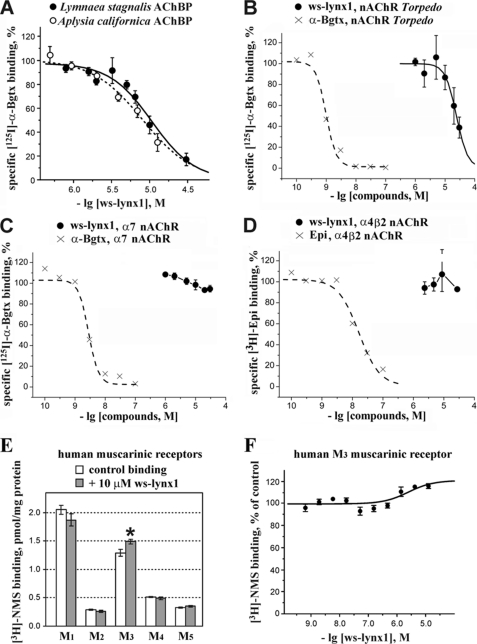
FIGURE 3.
Binding of ws-LYNX1 to AChBPs and nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Competition of ws-LYNX1 with 125I-α-Bgtx for binding to Ls-AChBP and Ac-AChBP (A), to membrane-bound nAChR from T. californica (B), and to α7 nAChR in the GH4C1 cell line (C). Competition of ws-LYNX1 with [3H]epibatidine for binding to α4β2 nAChR in the SH-EP1 cell line is shown in D. For comparison, the displacements of 125I-α-Bgtx and [3H]epibatidine by unlabeled Bgtx and epibatidine are also shown in these panels. Each point is mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. The Hill equation (y = 100/(1 + ([toxin]/IC50)nH)) was fitted to normalized data (% of control binding). The calculated parameters IC50 and nH were 10.7 μm and 1.5 for Ls-AChBP, 9.4 μm and 1.2 for Ac-AChBP, and 24 μm and 2.3 for muscle-type nAChR. E, effects of 10 μm ws-LYNX1 on [3H]NMS binding at M1–M5 human muscarinic receptors expressed in membranes of CHO cells. The asterisk indicates that binding of [3H]NMS to the M3 receptor in the presence of ws-LYNX1 was significantly different from control (p < 0.05, according to t test). Each point is mean ± S.E. of quadruplicates. F, interaction of ws-LYNX1 with [3H]NMS binding at muscarinic M3 receptor. Membranes expressing M3 muscarinic receptor (5 μg of protein) were incubated in the presence of indicated concentrations of ws-LYNX1 and 108 pm [3H]NMS. [3H]NMS binding is expressed in percent of control binding in the absence of ws-LYNX1. Each point is mean ± S.E. of quadruplicates. The equation (y = 100 × ([NMS] + Kd)/([NMS] + Kd × (Ka + 10[ws-LYNX1])/(Ka + 10[ws-LYNX1]/α)) was fitted to normalized data (% of control binding). Kd of [3H]NMS binding (207 pm) was determined in parallel saturation experiment. Estimated parameters are Ka (equilibrium dissociation constant of ws-LYNX1) 3.0 μm and a factor of cooperativity (α) of 0.8. The correlation coefficient of the fit is 0.8.