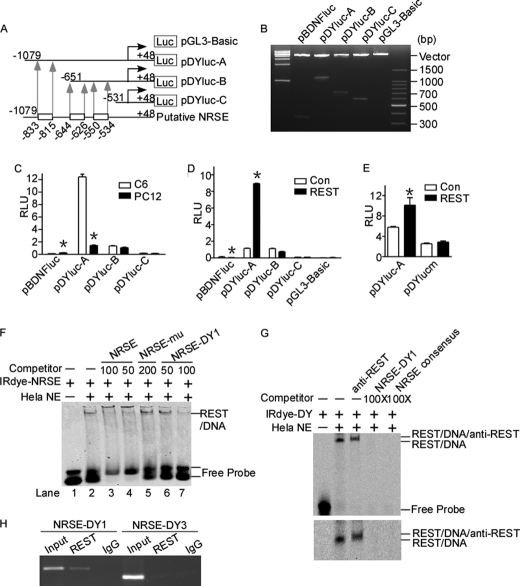
FIGURE 2.
Identification of a functional NRSE site in human DYRK1A promoter. A, schematic diagram of the human DYRK1A promoter deletion constructs consisting of a 5′-flanking region with serial deletions cloned into pGL3-Basic in front of the luciferase gene (Luc). Arrowheads indicate the directions of transcription. The numbers represent the end points of each construct. The positions of three putative NRSE sites are shown at the bottom. B, the deletion plasmids were confirmed by sequencing and restriction enzyme digestion checking on a 1.5% agarose gel. Vector size is 4.7 kb, and the DYRK1A gene 5′-flanking fragment inserts range from 0.5 to 1.5 kb. C, the deletion plasmids were transfected into REST-competent C6 or REST-incompetent PC12 cells. Plasmid pRL-TK was used to normalize the transfection efficiency, and luciferase activity was measured at 24 h by a luminometer. The values represent the means ± S.E. (n = 5). *, p < 0.001 by Student's t test. D, PC12 cells were co-transfected with REST expression vector and various DYRK1A promoter deletion constructs. Luciferase assay was performed 24 h after transfection. The values represent the means ± S.E. (n = 5). *, p < 0.001 by Student's t test. E, pDYlucm was made to contain the mutant NRES site of DYRK1A promoter. The mutant plasmid, as well as the wild type pDYluc-A, was co-transfected with REST expression plasmid into HEK293 cells. Plasmid pRL-TK was used to normalize the transfection efficiency, and luciferase activity was measured at 24 h by a luminometer. The values represent the means ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.01 by Student's t test. F and G, EMSA was performed with IRDye 700-labeled consensus NRSE oligonucleotides (F) or NRSE site of DYRK1A promoter (G). First lane, labeled probe without nuclear extract. Second lane, incubation of infrared labeled NRSE probe with HeLa nuclear extracts retarded the migration rate of the labeled probe, which formed a new shifted DNA-protein complex band. The addition of anti-REST antibody further shifted the band to a larger mass shown by a longer running time (third lane in the lower panel of G). Competition assays were performed by further adding different concentrations of molar excess of unlabeled competitive oligonucleotides. H, anti-REST antibody was used to immunoprecipitate the cross-linked REST-DNA complex in ChIP assay in SH-SY5Y cells. A pair of primers targeting DYRK1A was used to amplify NRSE-DY1 and NRSE-DY3. Signals amplified from input were used as size markers. Mouse IgG was used as a negative control. Con, control.