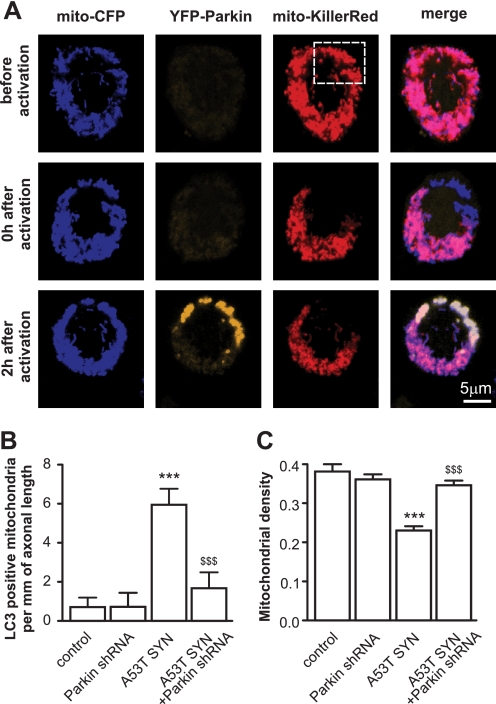
FIGURE 5.
The role of Parkin in mutant A53T α-synuclein-induced mitochondrial removal and mitochondrial loss. A, PC12 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing mito-CFP, YFP-Parkin, and mito-KillerRed. A subpopulation of mitochondria was then irradiated with 561 laser line, which caused a bleaching of the KillerRed signal. Two hours later, YFP-Parkin was localized to these mitochondria. For panels B and C, cortical neurons were transfected with plasmids expressing mutant A53T α-synuclein, EGFP or EGFP-LC3, mito-pDsRed2, and plasmids expressing shRNA against Parkin per the indicated combinations. B, suppression of Parkin inhibits mutant A53T α-synuclein-induced mitochondrial removal (Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's test). A plasmid encoding scrambled shRNA was used as a control for all of the shRNA experiments. C, suppression of Parkin also protects neurons from mutant A53T α-synuclein-induced mitochondrial loss (one way ANOVA followed by Newman Keuls test; interaction in all cases p < 0.0001, two way ANOVA). ***, p < 0.001 versus control, and $$, p < 0.01; $$$, p < 0.001 versus mutant A53T α-synuclein.