Figure 12. A schematic diagram of likely retinal and central influences on the four hypothalamic light-response types.
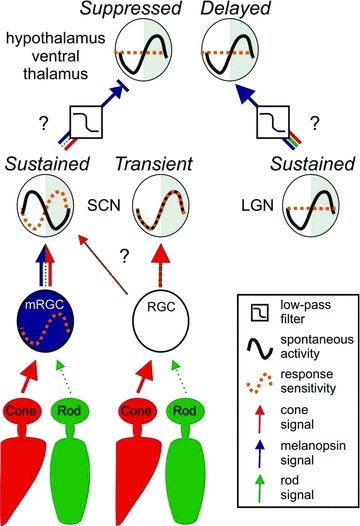
A model illustrating how photoreceptor signals, retinal/central clocks and central processing interact to produce the distinct properties of light responsive units detected in the hypothalamus. Cone: retinal cone photoreceptor; rod: retinal rod photoreceptor; mRGC: melanopsin retinal ganglion cell; RGC: conventional retinal ganglion cell; SCN: suprachiasmatic nuclei; LGN: lateral geniculate nuclei; Sustained: hypothalamic cell with sustained response type; Transient: hypothalamic cell with transient response type; Suppressed: hypothalamic cell with suppressed response type; Delayed: hypothalamic cell with delayed response type.
