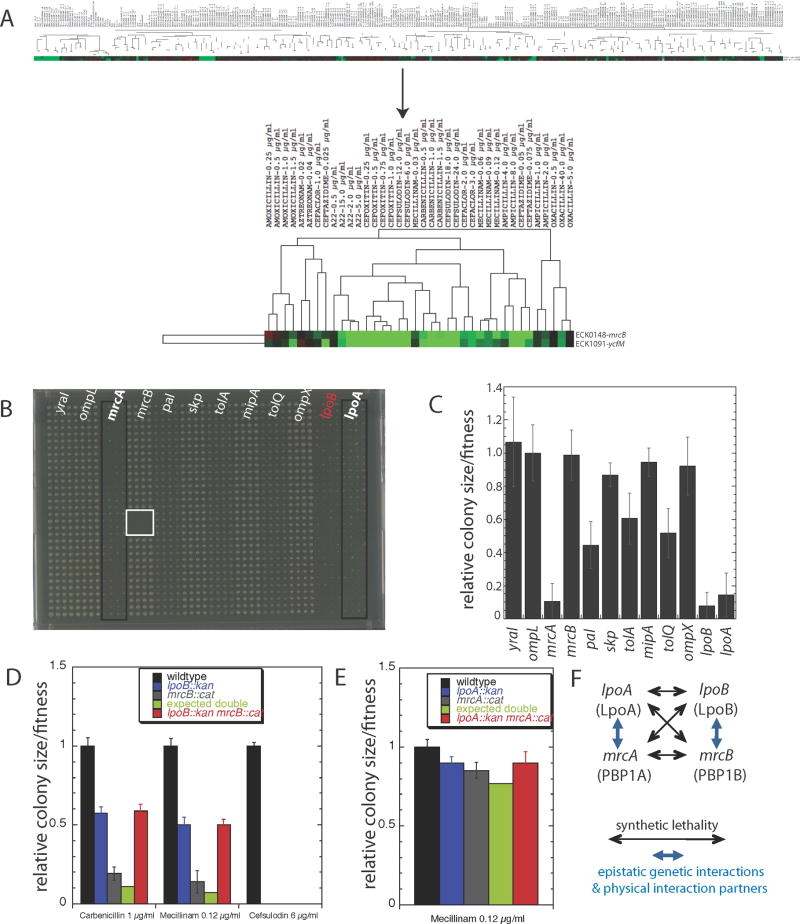
Figure 1.
Identification of two OM lipoproteins that regulate the activity of the major E. coli PG synthases. A. The growth phenotypes of lpoB− (ycfM) and mrcB− cluster strongly across 324 different conditions (cc = 0.9; p<10−116). Cellular fitness is depicted using a color scale: red (increased); green (decreased) fitness. The upper panel illustrates that the highly correlated growth phenotypes of the two mutant strains depend on strong responses to only a few of the 324 conditions tested; the lower panel (blow-up) shows that these conditions are sub-lethal doses of β-lactams (target TPase domain of PBPs) and A22 (targets MreB). B–C. lpoB− is synthetically lethal with both mrcA− and lpoA−. Using high-throughput Hfr mating, we produced a 12 × 12 genetic interaction matrix. Results from pseudo-Hfr lpoB::cat crossed with 12 KanR recipients arrayed in 1536 format (boxes of 4 × 32 = 128 replicas) on LB are shown in (B) and quantified in (C). Recipients are indicated above the double mutant plate (B) and have colony sizes similar to the wildtype as single mutants (data not shown); the self mating control (lpoB::cat x lpoB::kan; red), demonstrates the low false-positive rate, since a double mutant of the same gene cannot be made in haploid organisms; the white box is a sterility control. lpoB− is synthetically lethal with mrcA− and lpoA−, and synthetically sick with deletions of all tol-pal components. The other 6 genetic interactions are neutral. Error bars depict standard deviations (n = 128). lpoA− is synthetically lethal with both mrcB− and lpoB− (Fig. S1A–B). D–E. lpoB− and lpoA− show epistatic genetic interactions with mrcB− (D) and mrcA− (E) respectively. Quantifications of growth of wildtype, single mutant and the double mutant strains arrayed in 384-format (n = 96 colonies each) on LB agar plates containing different antibiotics (from Fig. S1C–F). Double mutant phenotypes are similar to single lpo mutant phenotypes indicating that each Lpo protein is absolutely required for the activity of its cognate PBP. F. Summary of genetic and physical interactions between Lpo proteins and PBP1A–PBP1B.