| HR (beats/min) |
 , with tM1 and tM6 in seconds , with tM1 and tM6 in seconds |
| A (Ohm) | Rheographic Index of pulse volume as determined from the maximum height of the systolic portion of the IPG waveform (A) when converted to Ohm resistance |
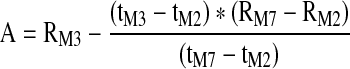 |
|
| B (Ohm) | Height of the IPG waveform at the dicrotic notch when converted to Ohm resistance |
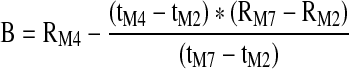 |
|
| C (Ohm) | Height of the IPG waveform at the dicrotic notch when converted to Ohm resistance |
 |
|
| DCI (% Ohm) | Dicrotic Index of arteriolar tone calculated as the ratio of C/A |
| DSI -(% Ohm) | Diastolic Index of venular tone calculated as the ratio of B/A |
| ST (Ohm-sec) | Total area under the selected IPG pulse waveform from the start of the pulse at tM2 to the start of the next pulse at tM7: |
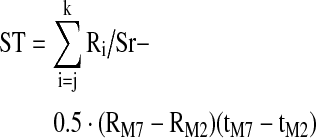 |
|
| Where j is the index for the IPG resistance datum at tM2, k is the corresponding index at tM7, and Sr is the sample rate (s–1) | |
| R0 (Ohm) | Average base resistance of the monitored segment during the IPG pulse given by 
|
| EXHT (Ohm) | Extrapolated IPG pulse amplitude given by the Nyboer25 back-projection: |
 |
|
| BF (ml/min) | BF segmental blood flow (calculated according to Nyboer)25 |
| BF = HR * EXHT * ρ *L2/R02 | |
| where ρ is the specific resistivity of blood 150 Ohm-cm22,25 and L (cm) is the separation distance between the two segmental sensing electrodes | |
| BFN (ml/min · ml) | Normalized segmental blood flow given by |
| BFN = BF/Vg | |
| where Vg = C2 L/4π is the segmental geometric volume with C (cm) as the measured maximum circumference of the monitored segment | |
| PTT (sec) |
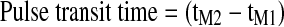 , is the time interval between the ECG QRS complex immediately preceding the selected IPG pulse and the start of the selected IPG pulse.24 , is the time interval between the ECG QRS complex immediately preceding the selected IPG pulse and the start of the selected IPG pulse.24
|
| PDNPTT (sec) | Post dicrotic notch pulse transit time = (tM5 − tM1) calculated as the time interval between the ECG QRS complex and the time of the occurrence of the maximum IPG pulse amplitude following the dicrotic notch |
| TIN (sec) |
 , the time period from start of the IPG pulse until the occurrence of the dicrotic notch27 , the time period from start of the IPG pulse until the occurrence of the dicrotic notch27
|
| TOUT (sec) |
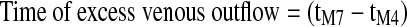 , the time period from the dicrotic notch until the end of the IPG pulse27 , the time period from the dicrotic notch until the end of the IPG pulse27
|
| TRATIO (%) | Ratio of TIN to TOUT |
| C Index | Jacquy's Capacitance—C Index20 1/sec or regional vasomotor capacitance. |
| AVE R–Ohm | Average base resistance during the IPG pulse duration |
| LI–DEG | Initial angle (between 0 and 10% of systolic amplitude) of IPG systolic rise |
| VOI–% SEC | Ratio of the time period between the maximum IPG pulse amplitude and the dicrotic notch to the total IPG cycle time |
| BFVE (ml/min.L) | Blood flow rate (ml/min) per liter of total arm segment volume (Ve) monitored during each test = BF/Ve |
| BFPct (ml/100 ml/min) | Percent blood flow rate (ml/min) per 100 ml of arm tissue = BFVE/100 |
| Note that A, ST, and EXHT are measures of pulse morphology independent of heart rate. In contrast, BF includes the influence of heart rate. The calculated output parameter values from RheoSys were stored in Excel spreadsheet format for statistical analysis. |

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.