Table 5.
Rate and Equilibrium Constants for Carbon Deprotonation of Glycine and Glycine Derivatives in Water at 25 °C and I = 1.0 (KCl)
| Carbon Acid | kHOa (M−1s−1) | pKab | Carbon Acid | kHOa (M−1s−1) | pKab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
4.5 × 10−5 c | 28.9c | 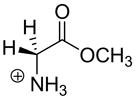 |
4.1c | 21.0c |
 |
3.3 × 10−4 c | 27.3c | 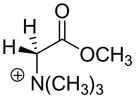 |
390c | 18.0c |
 |
2.9 | 21.9 | 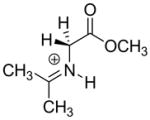 |
9.0 × 103 d | 14d |
 |
2.0 × 10−4 | 27 |  |
ca. 1 | ca. 23 |
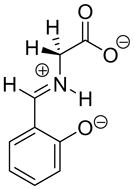 |
0.13 | 25 |  |
1.1 × 104 d | 14d |
 |
not determined | ca. 23 e |  |
7.5 × 102 f | 17f |
Second-order rate constant for deprotonation of the carbon acid by hydroxide ion calculated from data reported in this work, unless noted otherwise.
pKa for ionization of the carbon acid in water calculated from data reported in this work, unless noted otherwise.
Data from ref 2.
Data from ref 28.
Estimated as described in the text.
Data from ref 29.
