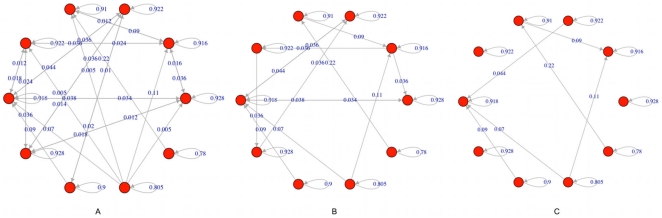
Figure 1. Attractor transition graphs in a RBN.
Circles represent network attractors; arrows represent transitions among attractors induced by single spin flips. All the nodes of all the states of each attractor are perturbed one by one; the numbers on each arrow are the fractions of cases where the corresponding transition is observed, so they provide an estimate of the probability that, by flipping at random the state of a node in an attractor, that transition takes place. In (a) the complete attractor transition graph is shown, while in (b) and (c) only those links which correspond to above-threshold transitions are retained (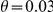 in (b) and
in (b) and 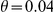 in (c)).
in (c)).