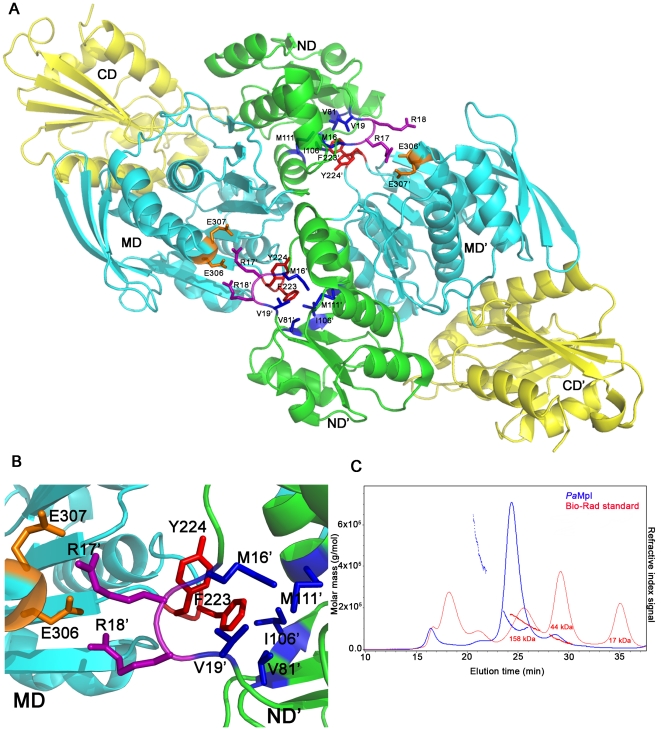
Figure 7. Oligomerization states of EcMurC and PaMpl.
(A) The dimer observed in the crystal structure of EcMurC (PDB 2f00) with the domains from each monomer labelled ND, MD, CD, and ND', MD', CD'; respectively, and the residues involved in dimer interactions highlighted as sticks. (B) A detailed view of the residues involved in intermolecular contacts: F223 and Y224 from the MD of one protomer interact with M16', V19', V81', I106' and M111' from ND' of the other protomer. E306 and E307 from one protomer interact with R17' and R18' from the other protomer. (C) Profile of the SEC/SLS experiment displaying the refractive index signal (SEC, continuous trace) against elution time (minutes) for PaMpl (blue) compared with a molecular weight standard (red, BioRad gel filtration standard with 158, 44 and 17 kDa peaks representing bovine γ-globulin, chicken ovalbumin and horse myoglobin, respectively). The discontinuous trace represents the molar mass (g/mol) calculated by SLS. For PaMpl, the SEC profile suggested a tetrameric form in comparison to the standard, but the more accurate molar mass estimated from SLS averaged across the majority of the peak was 120.5 kDa (as calculated by the ASTRA software (Wyatt Technology), with an oligomer number of 2.09, indicating a dimer as the dominant species in solution.