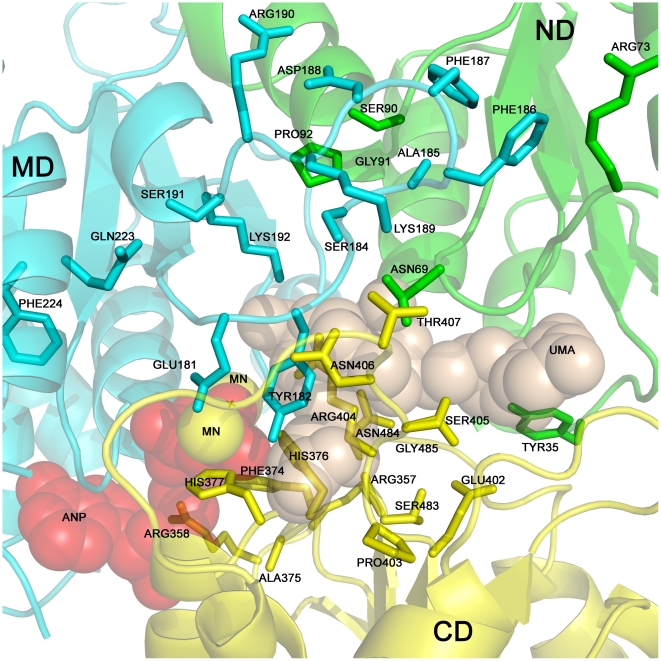
Figure 9. Additional Mpl-specific residues in ND, MD and CD that may be involved in substrate interactions.
Model of PaMpl bound to ANP, UMA and metal based on the superimposition of the ND and MD of PaMpl onto the corresponding domains from HiMurC (ND and MD are the most conserved domains between the proteins) bound to ANP and UMA (PDB id 1p3d). After superimposition, the ligand coordinates were transferred from HiMurC to generate the model of PaMpl bound to ligands. Numerous residues in the binding pocket are unique and conserved in Mpl proteins and could be involved in additional interactions with substrates. These include ND Tyr35, Asn69, Arg73 and Gly74 (not shown). Ser90, Gly91 and Pro92 pack against Mpl-specific loop consisting of Ser184 (Thr or Cys in different Mpl proteins), Ala185, Phe186, Phe187, Asp188 and Lys189. Tyr182, which is directly upstream of this loop, could also be involved in the recognition. Mpl-specific residues in CD are likely to play a crucial role in substrate specificity and include Arg357, Arg358, Phe374, Ala375, His376, His377, Glu402, Pro403, Arg404, Ser405 (in dual conformation), Asn406, Thr407, Ser483 (in dual conformation), Asn484 and Gly485.