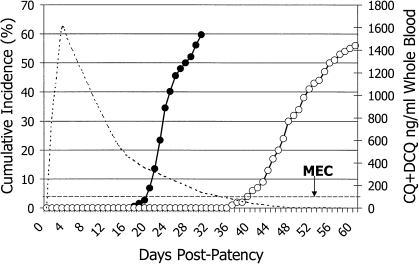
Figure 1.
The graph illustrates cumulative incidence (left axis) of relapse among several hundred patients infected with Plasmodium vivax from Southeast Asia and the Western Pacific regions and treated with either rapidly excreted quinine (solid points) or slowly excreted chloroquine (hollow points). Blood levels of chloroquine and its major metabolite desethylchloroquine (right axis) slowly decrease to below the minimally effective concentration (MEC) at approximately day 35, coinciding with commencement of relapse. Reproduced with permission from Baird [7]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2004; 48:4075–83. Copyright American Society for Microbiology.