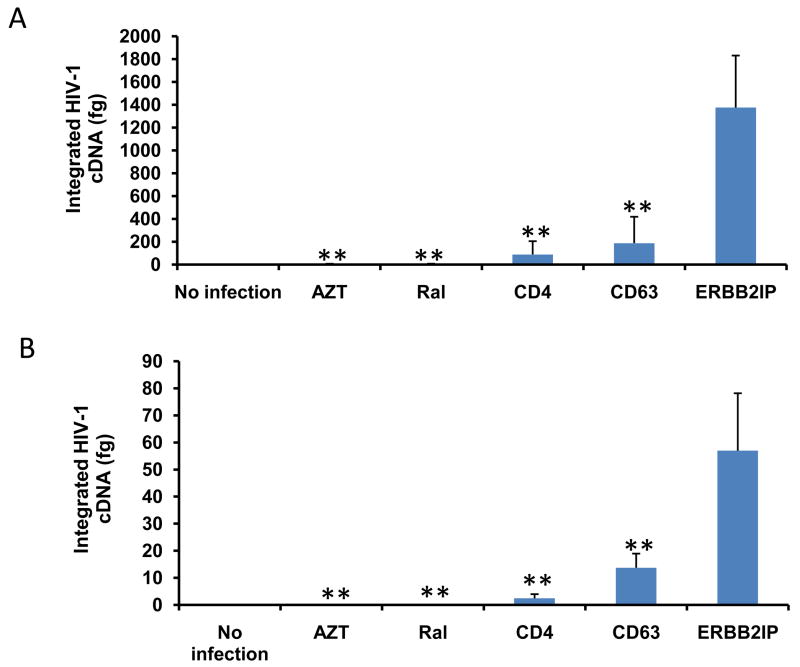
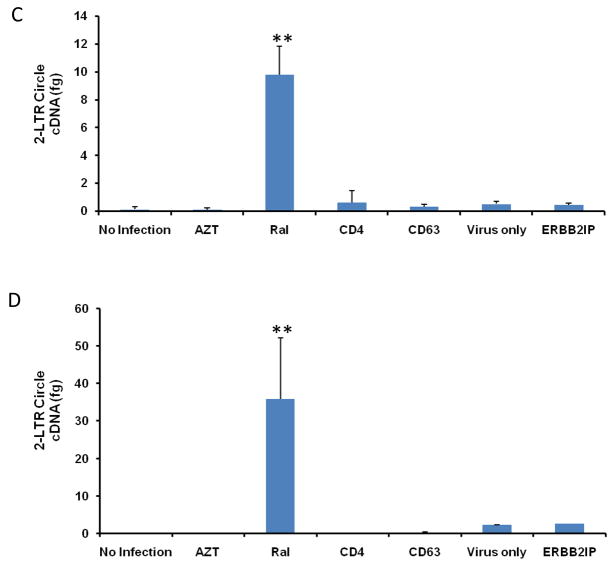
Figure 6. CD63 silencing decreases HIV-1 integration and 2-LTR circle formation in human MDMs and U373-MAGI-CCR5 cells.
(A) MDMs (5 × 105 cells/well) or (B) U373-MAGI-CCR5 cells (1 × 105 cells/well) were plated in 24-well plates and transfected with 50 nM siRNAs (CD63, CD4, and ERBB2IP). Controls include cells treated with raltegravir (20 mM) 24 h prior to infection, during infection and 48 h post- infection and untreated cells. Forty-eight hours post-transfection, cells were infected with HIV-1 SX (m.o.i. = 0.02). Genomic DNA was isolated from cells 5 days (MDMs) and 3 days (U373-MAGI-CCR5 cells) post-infection. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to quantify differences in HIV-1 SX integration between control cells and CD63-siRNA transfected cells using primers Alu-gag-LTR, and LTR probe (O’Doherty et al., 2002; Friedrich et al., 2010). Plasmid DNA was isolated from cells (C) 5 days (MDMs) and (D) 3 days (U373-MAGI-CCR5 cells) post HIV-1 SX infection. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to quantify differences between control cells and CD63-siRNA transfected cells using primers MH535/MH536 with probe MH603 to detect HIV 2-LTR circle formation (Butler et al., 2001; Friedrich et al., 2010). All experiments were performed in triplicate. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, compared with ERBB2IP group.