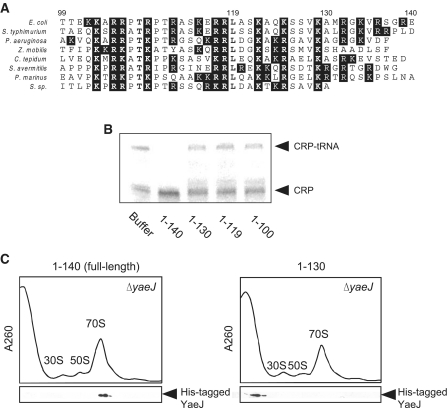
Figure 5.
C-terminal extension of YaeJ is required for PTH activity and ribosomal binding. (A) Sequence alignment of the C-terminal extension of YaeJ proteins from various bacteria. The C-terminal extensions that appeared unstructured in solution were determined according to the solution structure of the human YaeJ homolog, ICT1 (PDB code, 1J26) (21). White letters with a black background show basic amino acid residues. Bold letters indicate highly conserved residues. The numbering shown corresponds to the E. coli YaeJ protein. (B) Loss of PTH activity by truncation of the C-terminal extension of YaeJ. Wild-type YaeJ (1–140) and the three C-terminal truncation mutants (1–130, 1–119 and 1–100) were expressed using the in vitro translation system. Each of the mutant-containing samples was added to the translation reaction mixture using the non-stop-1 template. The final concentration of YaeJ and the mutants was 5 μM. (C) Ribosome association with His-tagged YaeJ and the C-terminal truncation mutant (1–130). His-tagged proteins were overexpressed in E. coli, and each was then added to the lysates of ΔyaeJ strain. After separation through a 5–20% sucrose gradient, fractions were analyzed by western blotting using an anti-His6 antibody.